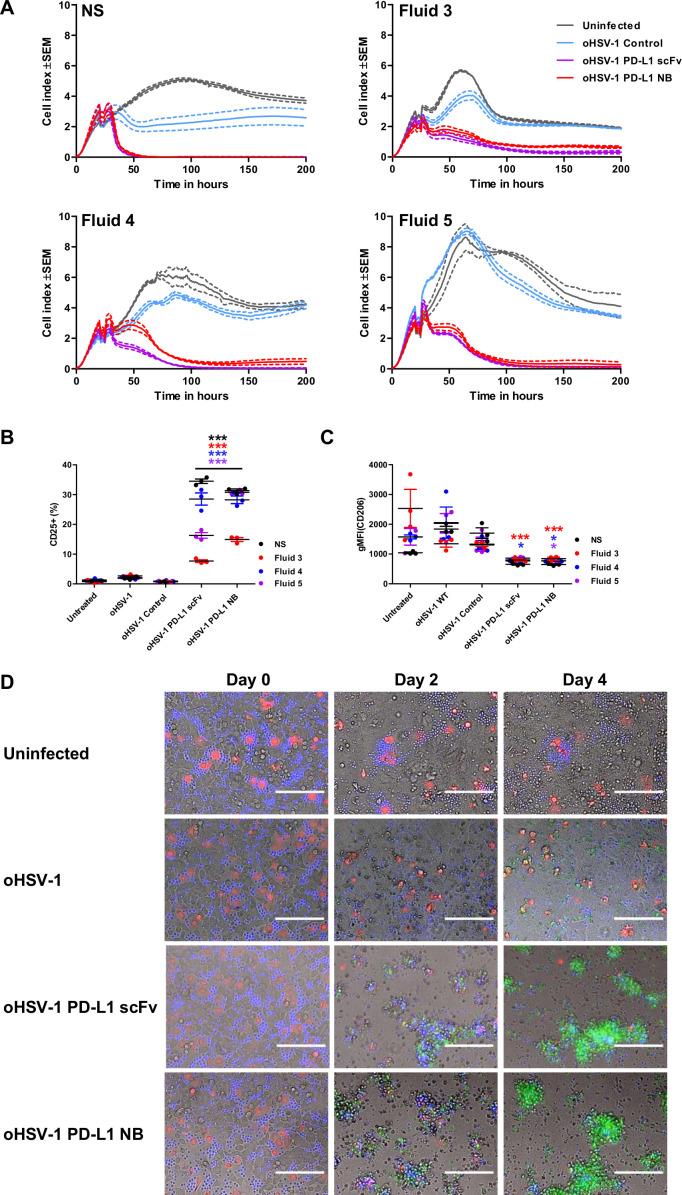
Figure 6.
oHSV-1 expressing PD-L1 BiTE can overcome immune-suppressive effects of ascites fluid and mediate killing of tumor cells and M2-like macrophages. (A) Cytotoxicity of BiTE-expressing oHSV-1 was monitored at 15 min intervals over 200 hours using xCELLigence. DLD-1 cells were infected with parental oHSV-1 or BiTE expressing oHSV-1 at an MOI of 1. PBMC-derived T cells (5:1) were added 3 hours postinfection in the presence of normal serum (NS) medium or ascites fluids (50% v/v). (B and C) Monocyte-derived macrophages from healthy donor PBMCs were polarized to M2-like macrophages using IL-10. After 48 hours of polarization, cells were infected with parental oHSV-1 or BiTE expressing oHSV-1 at MOI 1. Autologous T cells (1:5) were added 3 hours postinfection in the presence of NS medium or ascites fluids (50% v/v). Cells were analyzed by flow cytometry after 5 days for expression of CD25 (B) and CD206 (C). (D) Representative images of cocultures of DLD-1 carcinoma cells (unlabelled), polarized M2-like macrophages (red) and autologous CD3+ T cells (blue), infected with parental oHSV-1, oHSV-1 expressing PD-L1 scFv, PD-L1 NB BiTE or uninfected. Apoptosis was visualized using caspase-3 substrate (green). Scale bar: 1 mm. Full time-lapse sequences are displayed in online supplemental movies S1–S4. Statistical significance was assessed by two-way analysis of variance followed by Bonferroni post hoc analysis. Significance was assessed versus untreated cells within the relevant group (*p<0.05 and ***p<0.001). BiTE, bispecific T cell engager; NB, nanobody; oHSV-1, oncolytic herpes simplex virus-1; PD-L1, programmed death-ligand 1; scFv, single-chain variable fragment.