Figure 2. Lysosomes, mitochondria, and TBK1 in inflammation, immunometabolism and immune responses.
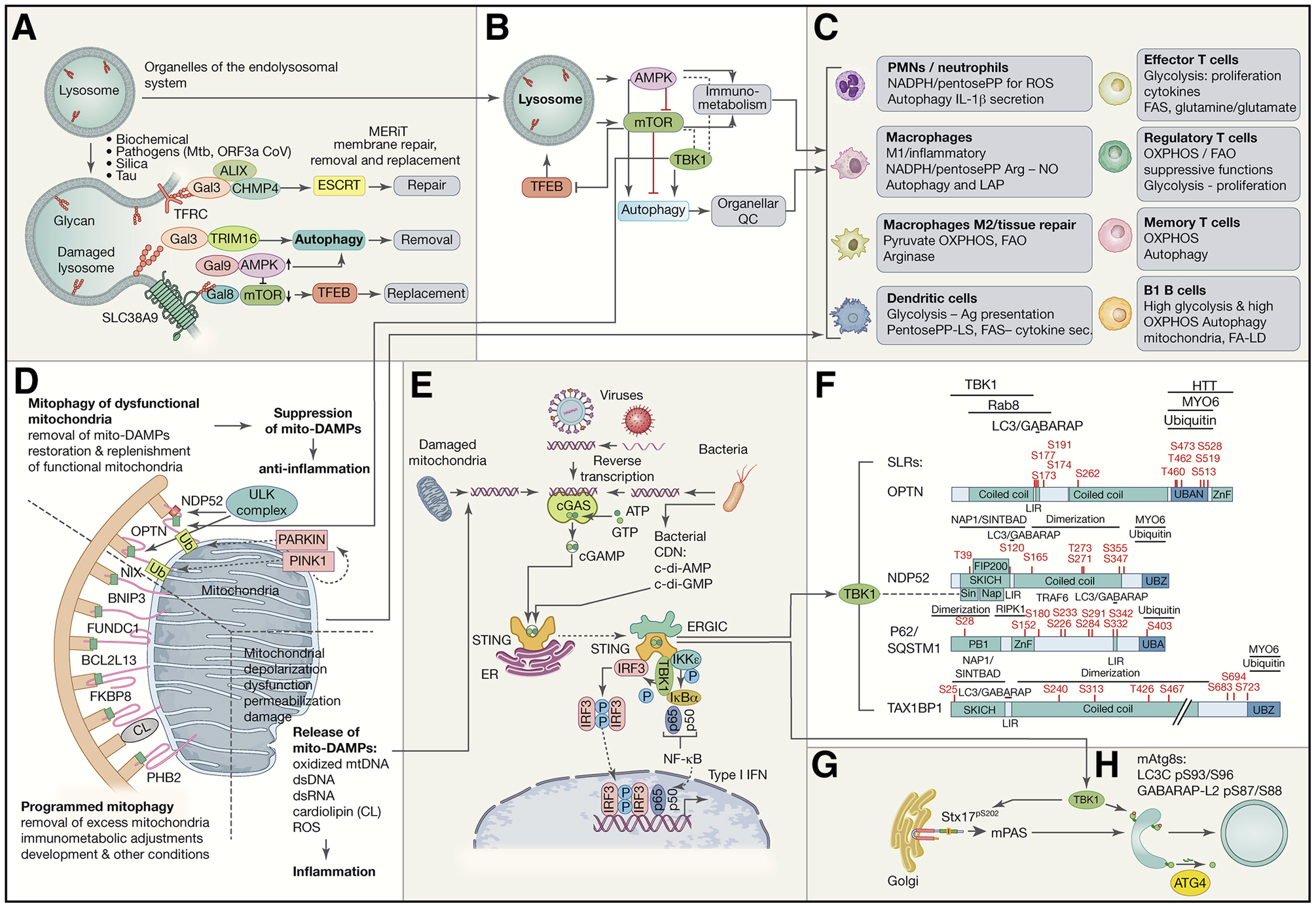
A. Lysosomal integrity is maintained by a system termed MERiT (membrane repair, removal and replacement). Galectins (Gal3, Gal8 and Gal9) recognize β-galactoside glycans exposed on cognate lysosomal membrane proteins: TFRC (transferrin receptor), SLC38A9, and LAMP1 and LAMP2 (not depicted) when lysosomal membrane is breached. They stimulate ESCRTs to repair lysosomes and AMPK to activate autophagy, whereas mTOR is inactivated. TRIM16 is one of lysophagy receptors. TFEB starts transcriptional program to replace lysosomes. B. Lysosome as the hub for AMPK, mTOR and TFEB, the three master regulators of autophagy, lysosomal system, metabolism and immunometabolism. Inhibitory and activating relationships are indicated and include TBK1 (which has positive and negative regulatory connections with AMPK and mTOR). C. Effects of signaling in B in different immune cells. D. Mitophagy, mitophagy receptors, and mitophagic suppression of inflammation caused by mitochondrial DAMPs (‘mito-DAMPs’). Dashed lines separate different types of mitophagy and proinflammatory signalng from damaged mitochiondria. Top, Pink1-Parkin system and receptors that participate in removal of dysfunctional mitochondria. Pink1 kinase and Parkin E3 ligase (phosphorylated by Pink1 to activate latent Parkin activity and recruit it to mitochondria) lead to ubiquitination and generation of phospho-ubiquitin which further amplifies Parkin activity leading to recognition of depolarized or damaged mitochondria by SLRs, NDP52 and OPTN, which bind ubiquitin. Bottom left, other mitophagy receptors act as integral membrane proteins of mitochondria and participate in mitophagy under developmental, differentiation or stress conditions. (E) Molecular machinery involved in STING-TBK1 activation in response to ectopic dsDNA, e.g. mitochondrial DNA that leaks into the cytosol (see panel D), DNA from pathogens (viruses and bacteria), etc. dsDNA binds to and stimulates cGAS that enzymatically generates cGAMP. STING stimulated by cGAMP (and other cyclic dinucleotides that may come from bacteria) activates TBK1. (F) TBK1 phosphorylates SLRs (F) modulating their ability to bind ubiquitin and mAtg8s such as LC3B, and possibly affecting other interactions. (G) TBK1 phosphorylates Syntaxin 17 (Stx17) involved in mPAS (mammalian pre-autophagosomal structure) and subsequent stages such as maturation. (H) TBK1 phosphorylates two members of the mAtg8 family rendering them resistant to delipidation by ATG4.
