Fig. 5. Hypoxanthine enhances expressions of OXPHOS-related genes via KID3.
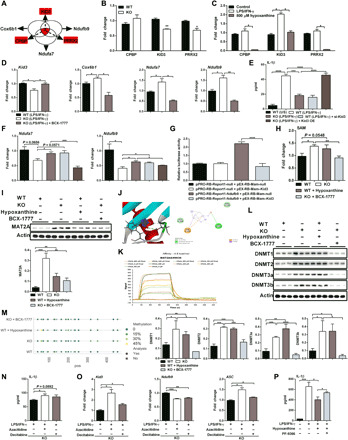
(A) Common TFs of Cox6b1, Ndufb9, and Ndufa7. (B and C) Gene expressions in proinflammatory macrophages [(B) n = 3] or in proinflammatory WT macrophages with hypoxanthine supplementation [(C) n = 3]. (D) Gene expressions in proinflammatory macrophages with BCX-1777 (10 μM) treatment (n = 3). (E and F) IL-1β secretion (E) and Ndufb9/Ndufa7 expression (F) in macrophages (n = 3). (G) Kid3 inhibits the luciferase activity of Ndufb9 promoter (n = 3 to 6). (H and I) Intracellular SAM (H) and MAT2A abundance (I) in macrophages (n = 3). (J) Molecular docking analysis of the complexes of MAT2A and hypoxanthine. (K) Hypoxanthine (H9636) directly interacts with MAT2A by SPR. (L) DNMTs abundance in macrophages (n = 3). (M) DNA total methylation level in promoter region of KID3 in macrophages (n = 3 and 4). (N and O) IL-1β secretion and gene expressions (O) from macrophages with azacitidine (500 nM) or decitabine (50 nM) (n = 3). (P) IL-1β secretion from WT macrophages with hypoxanthine combined PF-9366 (1 μM) (n = 3). Results represent two (B and C), three (G and H), four (D), or five (E and F) independent experiments. Data are shown as means ± SD (E, G, H, P, L, and N) or means ± SEM. Data were analyzed by unpaired t test (B) or two-way ANOVA with Bonferroni correction (C, D to I, L, and N to P). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, and ****P < 0.0001.
