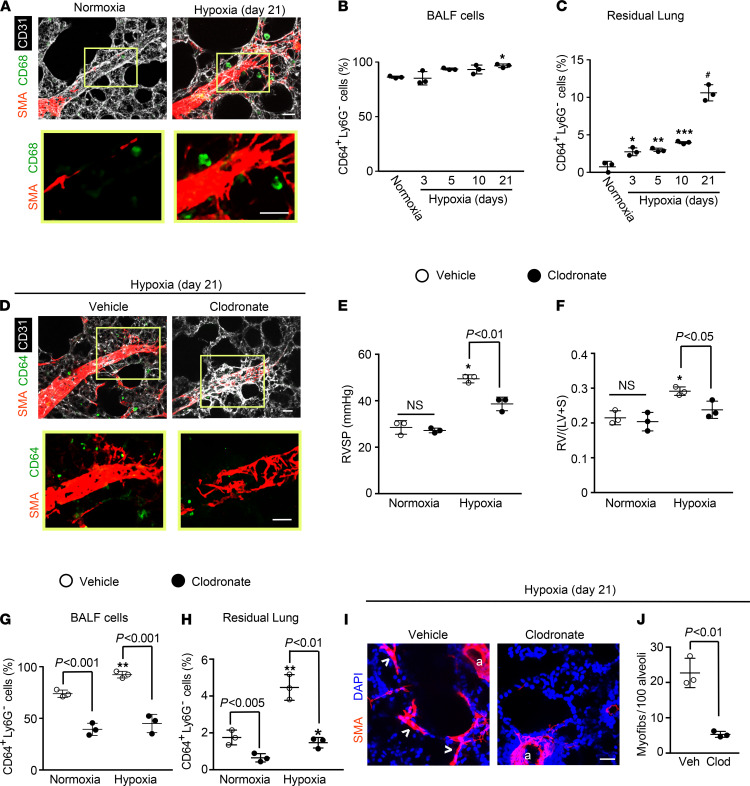
Figure 1. Lung macrophages accumulate with hypoxia and are critical for hypoxia-induced pulmonary vascular remodeling and PH.
WT mice were exposed to hypoxia (10% FiO2) for up to 21 days or maintained in normoxia as indicated. (A) Vibratome sections including distal arterioles of the L.L1.A1 regions of left lung were stained for markers of SMCs (α–smooth muscle actin [SMA]), macrophages (CD68), and ECs (CD31). The boxed region is shown as close-ups below. n = 6 mice. (B and C) BALF and residual lung were harvested, and single-cell suspensions were subjected to flow cytometric analysis. The percentage of total cells in the given compartment that are CD64+Ly6G– macrophages was determined. n = 3 mice per time point. (D–J) Liposomes containing PBS (vehicle) or clodronate were administered orotracheally at the onset of hypoxia (or normoxia as a control) and two times per week thereafter during the 21-day treatment. (D) Lung vibratome sections of the L.L1.A1.M1 region were stained for SMA, CD64, and CD31 with boxed regions magnified below. n = 4–5 mice. RVSP (E) and Fulton index (F; weight ratio of the right ventricle [RV] to sum of the left ventricle [LV] and septum [S]) are shown. n = 3 mice. (G and H) The percent of CD64+Ly6G– macrophages in total cells of the BALF and residual lung was determined. n = 3 mice. (I and J) Alveolar regions were stained for SMA and nuclei (DAPI), and the number of alveolar myofibroblasts (arrowheads) per 100 alveoli was determined. Arterioles are indicated by “a.” n = 3 mice. More than 500 alveoli were quantified per mouse. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test (*, **, ***, # vs. normoxia, P < 0.05, < 0.01, < 0.001, < 0.0001, respectively) was used in B, C, and E–H, and Student’s t test was used in J. Scale bars: 25 μm.