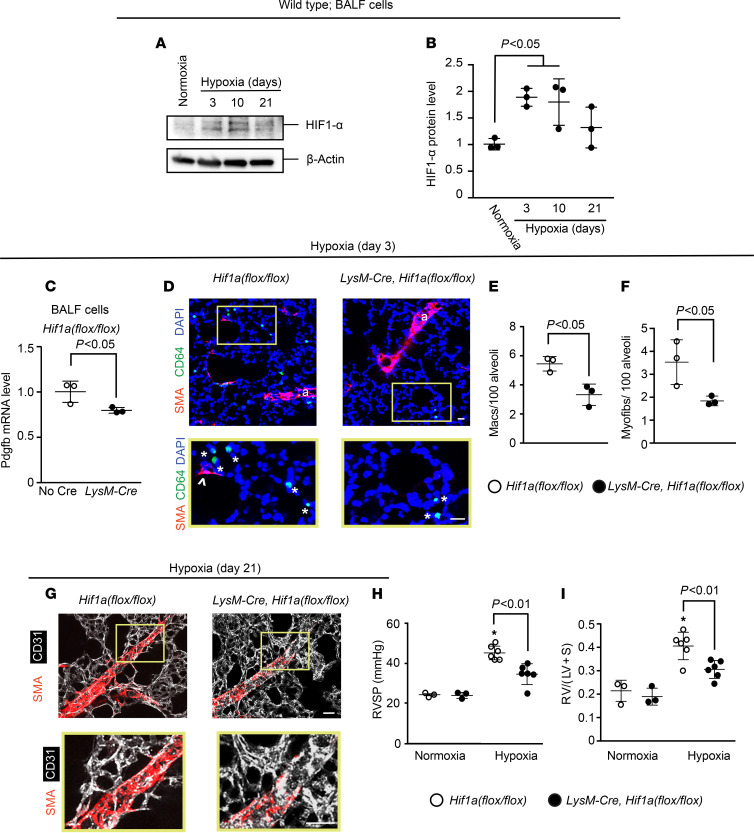
Figure 4. Hif1a deletion in myeloid cells attenuates hypoxia-induced Pdgfb expression, distal muscularization, and PH.
(A and B) BALF cells were isolated from normoxic or hypoxic (10% FiO2 up to 21 days) WT mice. HIF1-α and β-actin protein were assessed by Western blot (A) with densitometry of HIF1-α relative to β-actin (B). n = 3 mice per time point. (C–I) Hif1afl/fl mice also carrying no Cre or LysM-Cre were exposed to hypoxia for 3 or 21 days. At hypoxia day 3, Pdgfb transcript levels of BALF cells were determined by qRT-PCR (C). Lung vibratome sections were stained for SMA, macrophage marker CD64, and nuclei (DAPI) with arterioles indicated by “a” and boxed regions shown as close-ups below (D). The numbers of macrophages (asterisks) and alveolar myofibroblasts (arrowhead) were quantified per 100 alveoli (D–F). n = 3–5 mice; qRT-PCR was done in triplicate. More than 700 alveoli were quantified per mouse. At hypoxia day 21, vibratome sections with distal arterioles in the L.L1.A1.L1 area were stained for SMA and CD31 (G), and RVSP and the Fulton index were measured as shown (H and I). n = 3 mice. One-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple-comparison test was used in B, H, and I (* vs. normoxia, P < 0.05), and Student’s t test was used in C, E, and F. Scale bars: 25 μm.