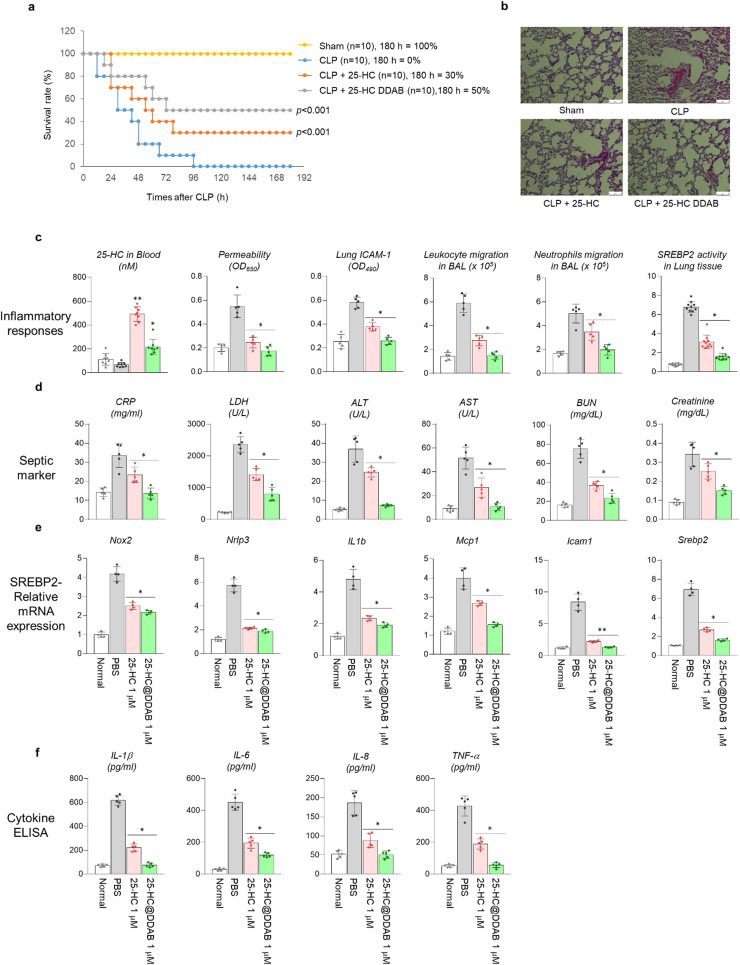
Fig. 3.
Effect of 25-HC and 25-HC@DDAB in the rescued survival rate of septic mice model. (a) Time-course survival rate of the cecal ligation and puncture (CLP) mice model after the treatment of 25-HC and 25-HC@DDAB (n = 10/each group). (b) Histological analysis of lung tissue from CLP mice models. The administration of 25-HC@DDAB reduced the blood vessel rupture and lung tissue damage. Representative images from each group are shown (n = 5). Scale bar, 100 µm. (c) Changes of inflammation-related signatures in mice models after the administration of 25-HC and 25-HC@DDAB after the CLP treatment. The in vivo signatures includes serum 25-HC level (n = 10), vascular permeability (n = 5), ICAM-1 (n = 5) level in lung tissue, leukocyte (n = 5) and neutrophil migration (n = 5) in bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL), and SREBP2 activity (n = 10) in lung tissue. (d) Changes of septic markers in the blood of 25-HC and 25-HC@DDAB treated CLP mouse models. The markers include CRP, LDH, ALT, AST, BUN, and creatinine (n = 5). (e) Changes of SREBP2-related mRNA expression after the treatment of 25-HC and 25-HC@DDAB. The mRNAs related to SREBP2 are Nox2, Nrlp3, IL1b, Mcp1, Icam1, and Srebp2 (n = 5). (f) Changes of cytokine levels after the treatment of 25-HC and 25-HC@DDAB in CLP mouse models. The cytokines include IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α (n = 5). Statistical analysis was performed using a two-tailed unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.