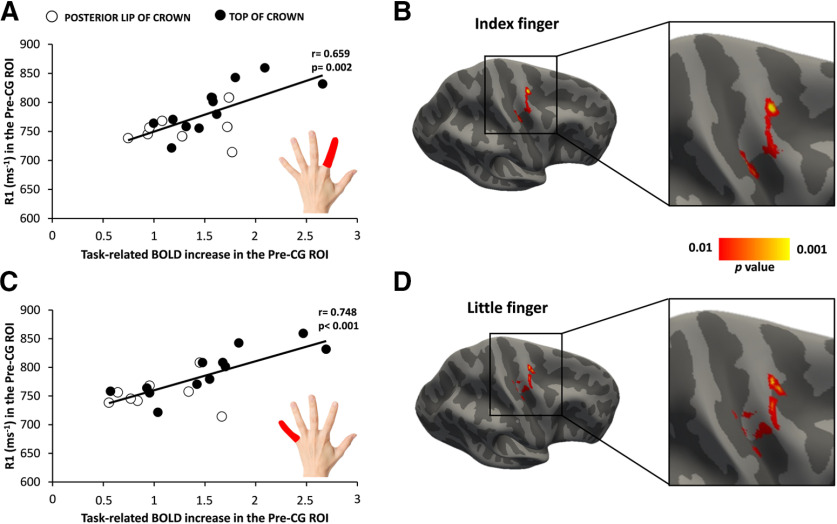
Figure 5.
A higher cortical myelin content in right precentral motor hand knob is associated with a higher functional activation during visually cued repetitive finger movements. Positive linear relationship between cortical myelination (as indexed by the mean R1 signal) in the precentral hand knob and the BOLD signal increase during the visuomotor abduction task. A, C, The same positive relationship became evident when the task was performed with the left index finger (A) or little finger (C). Open and closed black circles indicate subjects with hotspots located in the posterior lip of precentral crown and the top of the precentral crown, respectively. B, D, Surface-rendered statistical parametric maps: the maps show voxels with a significant positive relationship between the precentral myelin-related signal and the task-related BOLD increase for index finger (B) and little finger (D). Statistical maps are thresholded at p uncorrected < 0.01 for illustrative purposes.