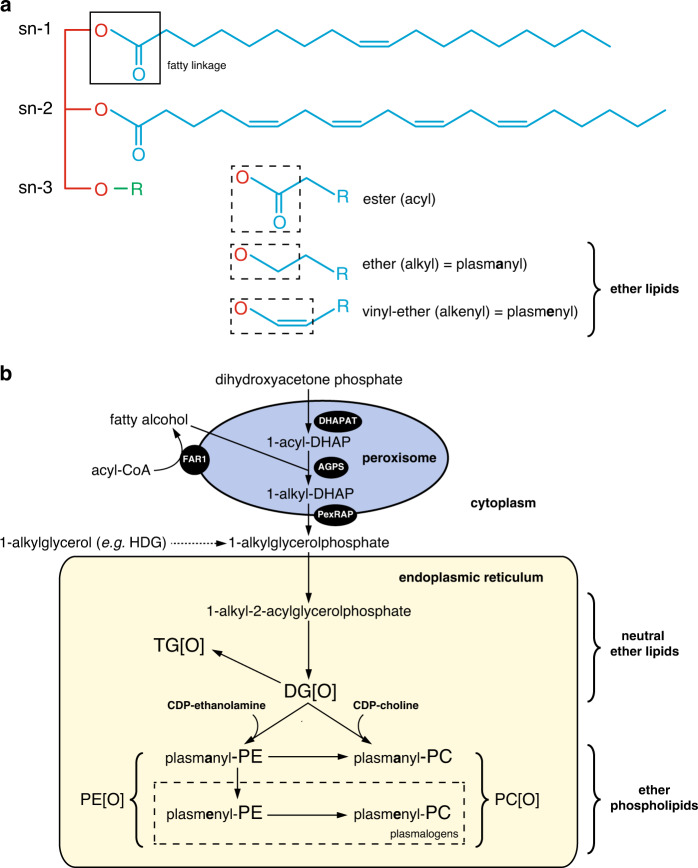
Fig. 1. Ether lipids and ether lipid metabolism.
a Molecular structures of glycerolipids and glycerophospholipids. These types of lipids contain a glycerol backbone (red) attached to one or two fatty acid/fatty alcohol (blue) substituents at the sn-1 and sn-2 position and a headgroup R (green) attached at the sn-3 position. When R is a hydrogen or a fatty acid the molecule is a glycerolipid; when R is a phosphate linked to a species characteristic headgroup (choline, ethanolamine, etc.) the molecule is a glycerophospholipid, also known as a phospholipid. In ether phospholipids, the fatty linkage at the sn-1 position is either an ether (plasmanyl) or a vinyl ether (plasmenyl); the latter substitution defines the subclass that is known as plasmalogens. In analogy to ether phospholipids, ether variants of glycerolipids also exist with an ether fatty linkage on the sn-1 position. b Ether lipid biosynthesis. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP)-acyltransferase (DHAPAT), esterifies DHAP at the sn-1 position with a long-chain fatty acyl-CoA yielding 1-acyl-DHAP. Next, alkylglycerone phosphate synthase (AGPS) replaces the acyl unit by a fatty alcohol, produced by reduction of an acyl-CoA by fatty acyl-CoA reductase 1 (FAR1), resulting in the formation of 1-alkyl-DHAP. 1-Alkyl-DHAP is then reduced to 1-alkylglycerolphosphate by acyl/alkyl-DHAP reductase (PexRAP), which is converted to 1-alkyl-2-acylglycerol (DG[O]) at the endoplasmic reticulum (ER). Exogenous 1-alkylglycerol (for example 1-hexadecylglycerol [HDG]) can be phosphorylated to 1-alkylglycerolphosphate, which then bypasses the peroxisomal steps in ether lipid biosynthesis. DG[O] can be converted to plasmanyl-PE and plasmanyl-PC by condensation with CDP-ethanolamine and CDP-choline, respectively. Creation of a vinyl ether by desaturation in the ER yields plasmenyl-PE, which can be converted to plasmenyl-PC, both of which are called plasmalogens. PC and PE ether phospholipids, thus including plasmanyl and plasmenyl-species, are collectively called PC[O] and PE[O], respectively. DG[O] can also be acylated which yields 1-alkyl-2,3-diacylglycerol (TG[O]).