Figure 2.
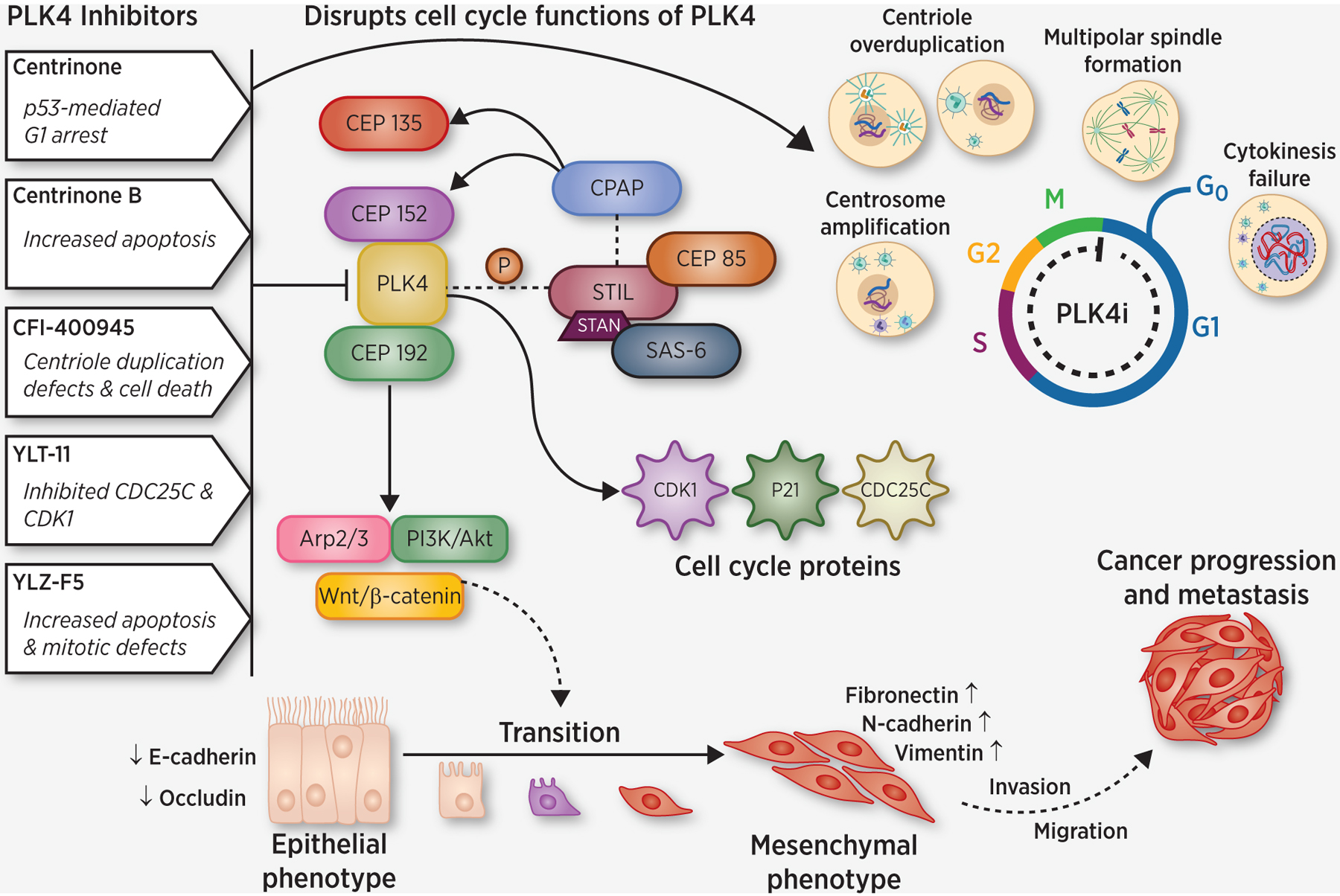
Schematic representation of PLK4 signaling in cancer with details of selected PLK4 inhibitors. Various PLK4 inhibitors along with their potential mechanisms to inhibit cancer progression are shown. PLK4 modulation, either by chemical/genetic inhibition, or overexpression, can disrupt cell cycle functions of PLK4, including induction of centrosome amplification through the simultaneous generation of multiple procentrioles adjoining each parental centriole during S phase of cell cycle leading to cancer progression. Various cellular proteins interact and complex with PLK4, leading to PLK4-mediated disruptions to cell cycle. Recent findings also suggest that PLK4 signaling is associated with epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which is well known to be linked to tumor invasion and metastasis. Visualization initially created with BioRender and professionally redrawn by the journal.
