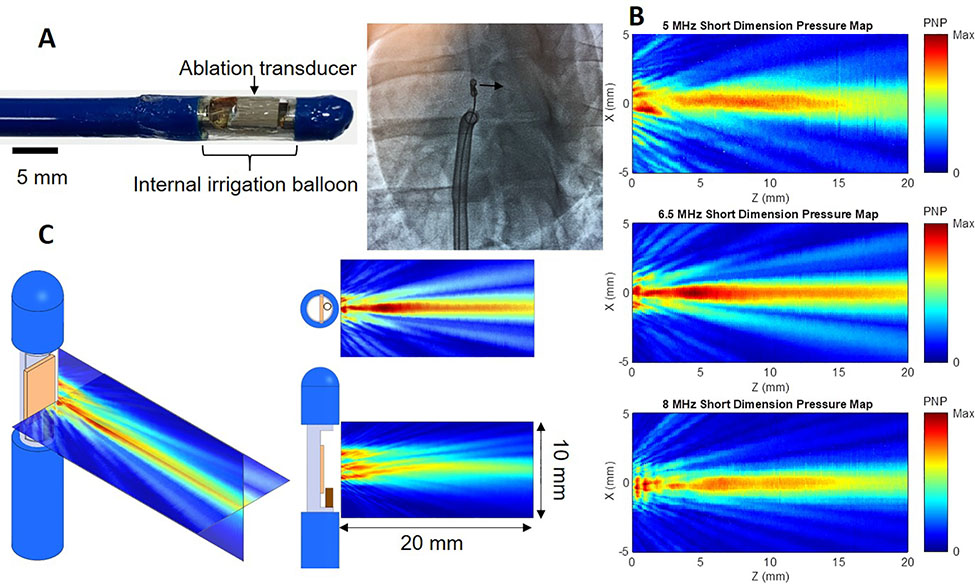
Figure 1.
High-intensity ultrasound (HIU) catheter and acoustic fields. A: 12 Fr internally-irrigated HIU catheters (A) were built and directed to the right ventricular septum under transthoracic echocardiogram and fluoroscopic guidance (left anterior oblique 15° view demonstrates transducer in profile and aiming toward the septum). B: Acoustic field maps measured using a needle hydrophone in degassed water, where the catheter surface is at Z = 0 mm and HIU pressure propagates in the positive Z direction, indicating the 6.5 MHz (middle) catheter to generate the deepest lesions and largest acoustic field. C: Further characterization of the 6.5 MHz HIU catheter’s acoustic field in two orthogonal planes.
PNP: peak negative pressure.