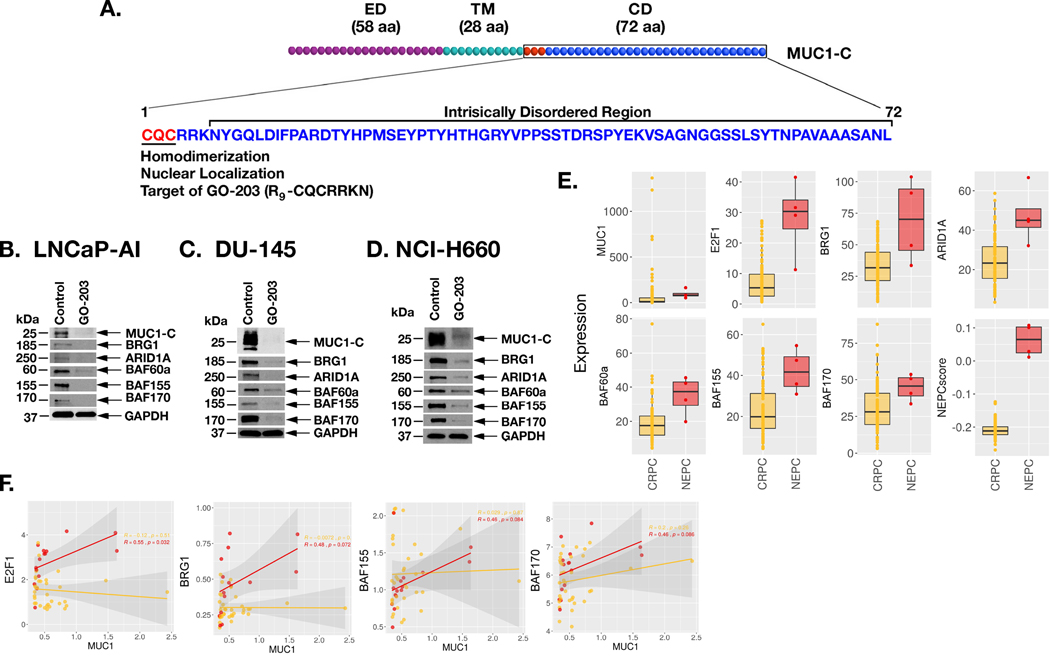
Figure 4. Targeting MUC1-C with the GO-203 inhibitor suppresses expression of BAF subunits.
A. Schema of MUC1-C depicting the 58 aa extracellular domain (ED), 28 aa transmembrane domain (TM) and 72 aa cytoplasmic domain (CD). MUC1-C homodimerization and thereby nuclear import is dependent on the CQC motif, which is targeted by the cell penetrating GO-203 inhibitor (R9-CQCRRKN). Downstream to the CQC motif is an intrinsically disordered region as found in multiple oncogenic proteins that function as nodes in integrating multiple signaling pathways linked to transformation. B-D. LNCaP-AI (B), DU-145 (C) and NCI-H660 (D) cells were left untreated or treated with 5 μM GO-203 for 48 h. Lysates were immunoblotted with antibodies against the indicated proteins. E. Analysis of the SU2C PC dataset comparing expression of the indicated genes and the NEPC score in CRPC and NEPC tumor samples. The asterisk (*) denotes a pvalue<0.05 (Wilcox-test). F. Analysis of the Beltran PC dataset assessing the correlation of MUC1 with expression of the indicated genes in CRPC (yellow) and NEPC (red) tumor samples.