Figure 4. Crotonate promotes endoderm differentiation of hESCs.
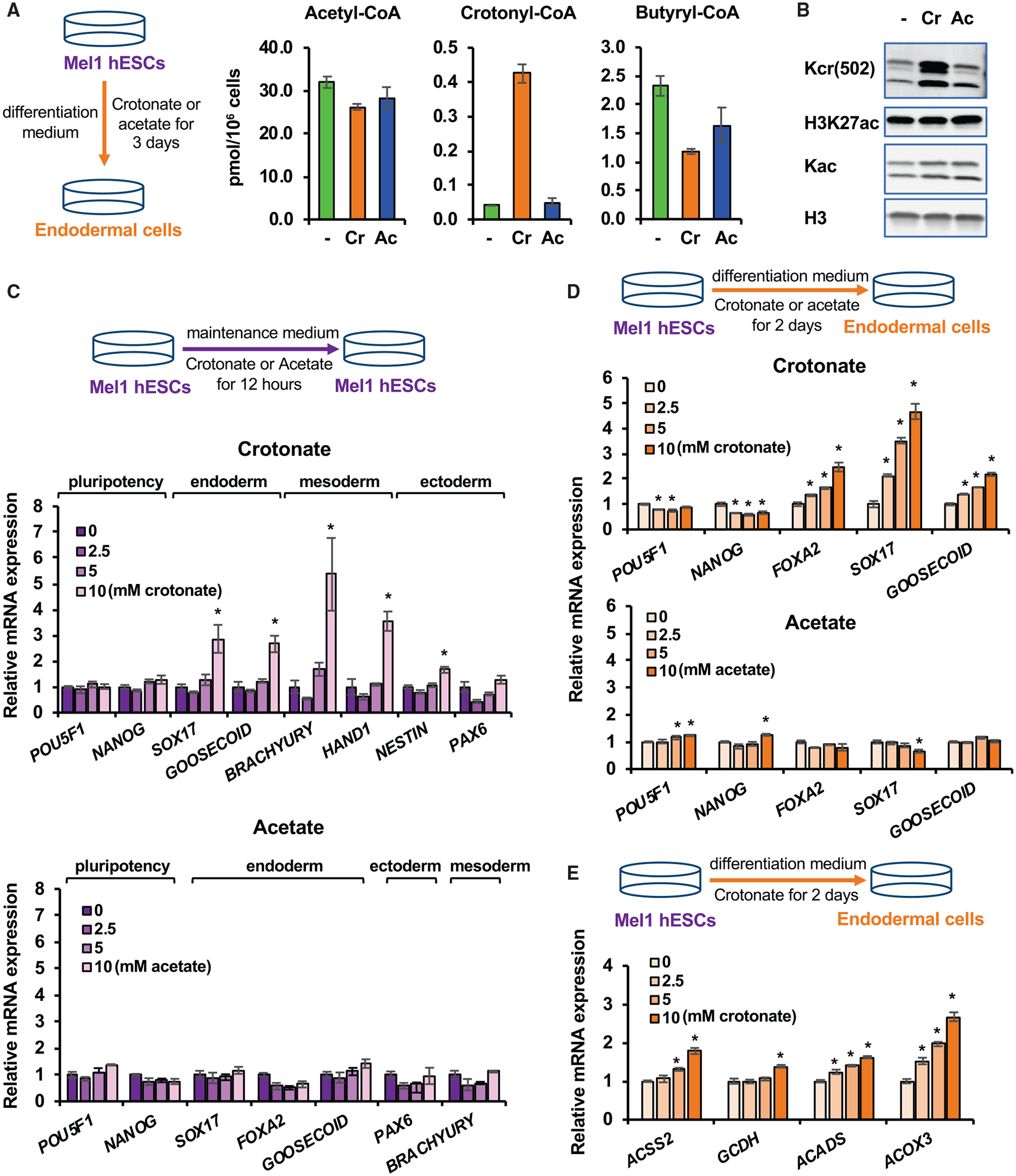
(A) Crotonate increases the cellular level of crotonyl-CoA. The concentrations of acetyl-CoA, crotonyl-CoA, and butyryl-CoA in mel1 hESCs after 3-day differentiation into endoderm in regular differentiation medium (−) or in differentiation medium containing 5 mM crotonate (Cr) or 5 mM acetate (Ac) were analyzed as described in Method details (n = 3 biological replicates/group, values are expressed as mean ± SEM).
(B) Crotonate increases histone crotonylation. Mel1 hESCs were induced for endoderm differentiation with or without 5 mM Cr or 5 mM Ac for 3 days. Whole-cell lysates were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies.
(C) Crotonate is sufficient to induce expression of endodermal and mesodermal genes in hESCs. Mel1 hESCs were treated with increased doses of Cr or Ac in ESC maintenance medium for 12 h, and the expression of the indicated genes was analyzed by qPCR (n = 3 biological replicates/group, *p < 0.05, values are expressed as mean ± SEM).
(D) Crotonate dose-dependently promotes the expression of endodermal genes upon endoderm differentiation of hESCs. Mel1 hESCs were induced to differentiate into endoderm in differentiation medium containing 0, 2.5, 5, or 10 mM Cr or Ac for the indicated days. The mRNA levels of the indicated genes were analyzed by qPCR (n = 3 biological replicates/group, *p < 0.05, values are expressed as mean ± SEM).
(E) Crotonate dose-dependently enhances the expression of key crotonyl-CoA-producing enzymes upon endoderm differentiation. Mel1 hESCs were differentiated into endoderm in regular differentiation medium containing 0, 2.5, 5, or 10 mM Cr for 2 days. The mRNA levels of the indicated crotonyl-CoA-producing enzymes were analyzed by qPCR (n = 3 biological replicates/group, *p < 0.05, values are expressed as mean ± SEM).
See also Figures S5A and S5B.
