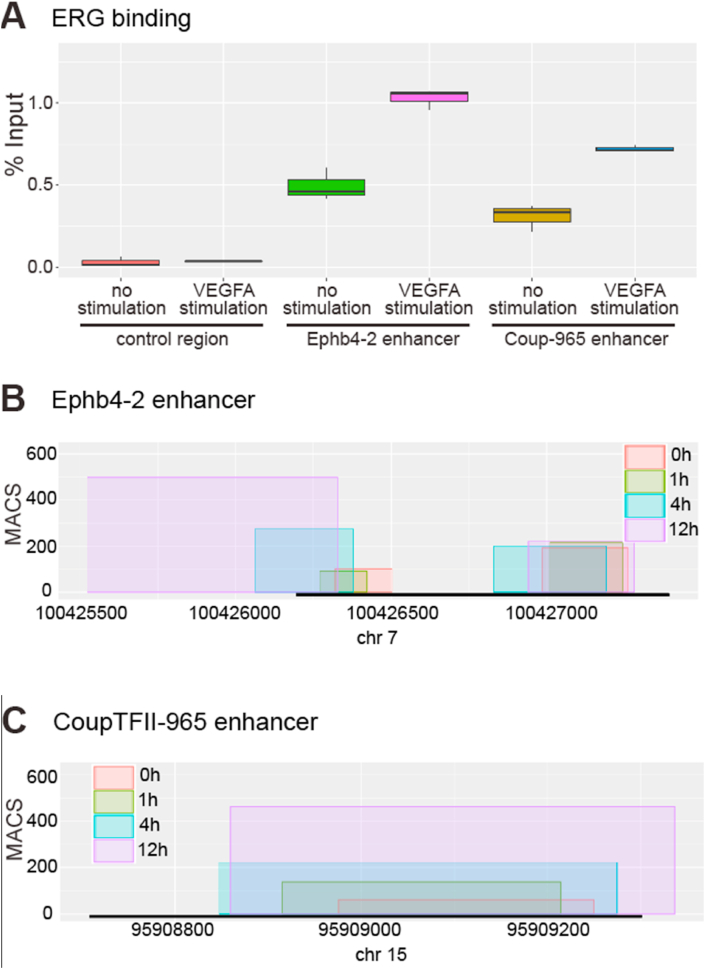
Fig. 4.
VEGFA signalling increases ETS factors binding to venous enhancers. A. HUVEC ERG binding ChIP-qPCR box-and-whiskers plot. ERG binding in unstimulated HUVECs is significantly enriched at the Ephb4-2 p < 0.001 (green) and CoupTFII-965 p < 0.001 (yellow) enhancers compared to the control region. Stimulation of HUVECs with VEGFA for 1.5 h prior to analysis resulted in significantly enriched ERG binding at both the Ephb4-2 p < 0.001 (pink) and CoupTFII-965 p < 0.001 (blue) enhancer regions compared to unstimulated conditions. No enrichment is observed between control regions (p = 1.000). The six conditions show significant differences (ANOVA f-test, p < 1 × 10-9). Horizontal lines = medians, boxes = interquartile range (IQR); vertical lines = minimal/maximal values. Data represents three biological replicates each with three technical replicates performed in triplicate. All data points were included in statistical analysis. Figure S9 shows the data presented alongside the IgG controls. B–C. ETS1 binding at venous Ephb4-2 (B) and CoupTFII-965 (C) enhancer regions is increased in the hours after VEGFA stimulation. Box width indicates region of ETS1 binding and box height indicates the maximal MACS score for this region after 0h (red), 1 h (green), 4 h (blue) and 12 h (purple) of VEGFA stimulation. Black bar indicates orthologous enhancer region and x axis covers a 5 kb genomic region. Numbers indicate distance from transcriptional start site (TSS) of the Ephb4 (B) or Coup-TFII (C) gene. Data reanalysed from ETS1 ChIP-seq by Chen et al., (2017). Fig. S10 shows the data for other enhancers.