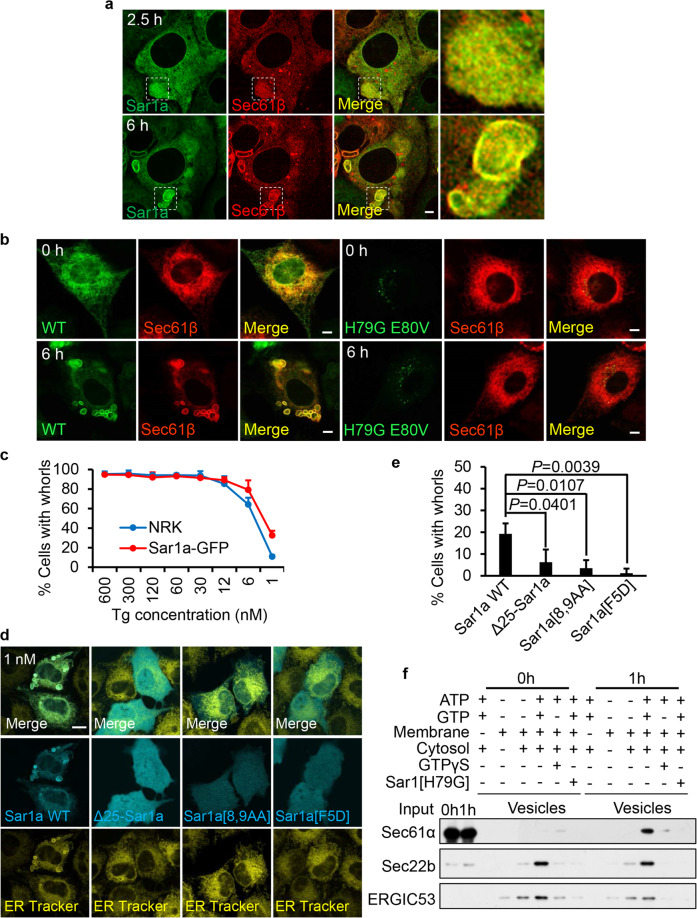
Fig. 4. Recruitment of Sar1 initiates formation of ER whorl precursors.
a Sar1a-GFP-expressing NRK cells transfected with RFP-Sec61β were treated with Tg for 2.5 or 6 h and then images were acquired by Opera Phenix microscopy with 60× confocal mode. Scale bar, 5 μm. The regions outlined with white dashed lines are magnified on the right (Merge). b RFP-Sec61β-expressing NRK cells were transfected with Sar1a-GFP (WT) or Sar1a[H79G]-GFP (H79G E80V). Cells were treated with Tg for 0 or 6 h, and then imaged with a confocal microscope. Scale bar, 5 µm. c NRK cells stably expressing Sar1a-GFP and NRK cells were treated with decreasing concentrations of Tg for 6 h, and then stained with ER-Tracker Red and visualized by confocal microscopy. Cells were quantified for ER whorls (n = 3 independent experiments; >100 cells were assessed per independent experiment). Data represent means ± SE. d NRK cells were transfected with Sar1a-GFP (Sar1a WT), Δ25-Sar1a-GFP, Sar1a[8,9AA]-GFP, or Sar1a[F5D]-GFP. Cells were treated with Tg (1 nM) for 6 h, and then stained with ER-Tracker Red and visualized by confocal microscopy. Scale bar, 10 μm. e Cells from d were quantified for ER whorls (n = 3 independent experiments; >50 cells were assessed per independent experiment). Data represent means ± SE. P values were calculated using a two-tailed, unpaired t-test. f Permeabilized NRK cells treated with Tg for 0 or 1 h were employed in an in vitro COPII budding assay. The resulting vesicle fractions and permeabilized cell input were separated by SDS-PAGE and visualized by immunoblotting.