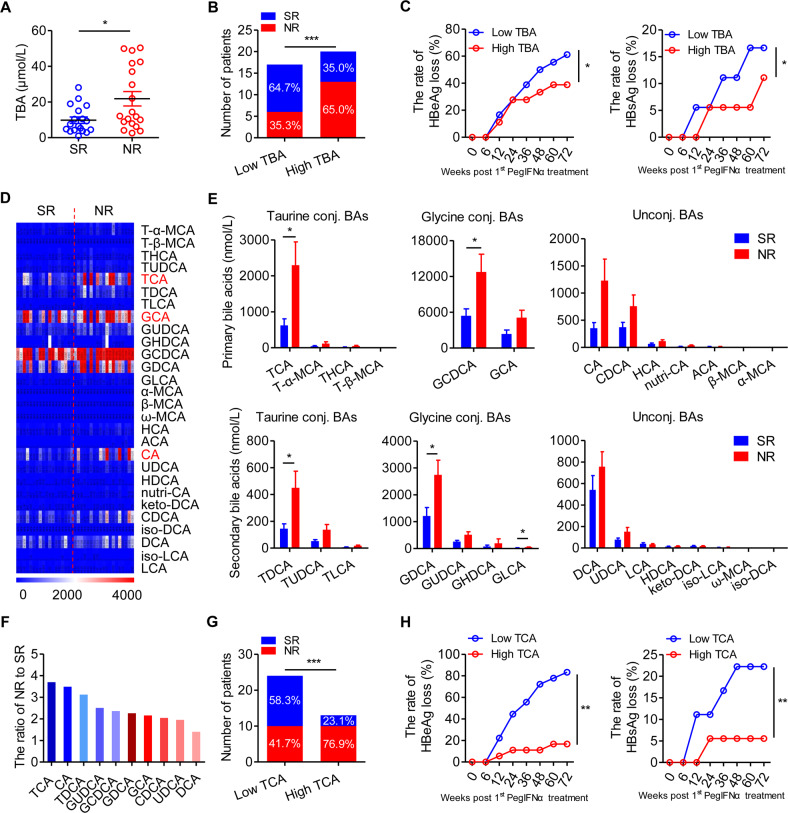
Fig. 2.
Taurocholic acid inhibits the response to interferon-α therapy in patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B. A The level of serum total bile acid (TBA) in the sustained response (SR; n = 18) and nonresponse (NR; n = 19) groups of HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients receiving pegylated interferon-alpha (PegIFNα) therapy. Mann–Whitney U test. B The number of SR and NR patients in the low TBA (n = 17) and high (n = 20) TBA groups. Chi-squared test. C The rate of HBeAg and HBsAg loss in the low TBA (n = 11) and high TBA (n = 7) groups in SR patients at the indicated time points after PegIFNα treatment. Two-way ANOVA. D Heatmap of serum BA profiles in SR and NR patients. E The level of BAs in the SR (n = 18) and NR (n = 19) groups. Mann–Whitney U test. F The level of BAs in the NR group relative to the SR group. G The number of SR and NR patients in the low taurocholic acid (TCA) group (n = 24) and high TCA group (n = 13). Chi-squared test. H The rate of HBeAg and HBsAg loss in the low TCA (n = 15) and high TCA (n = 3) groups in SR patients at the indicated time points after PegIFNα treatment. Two-way ANOVA. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001