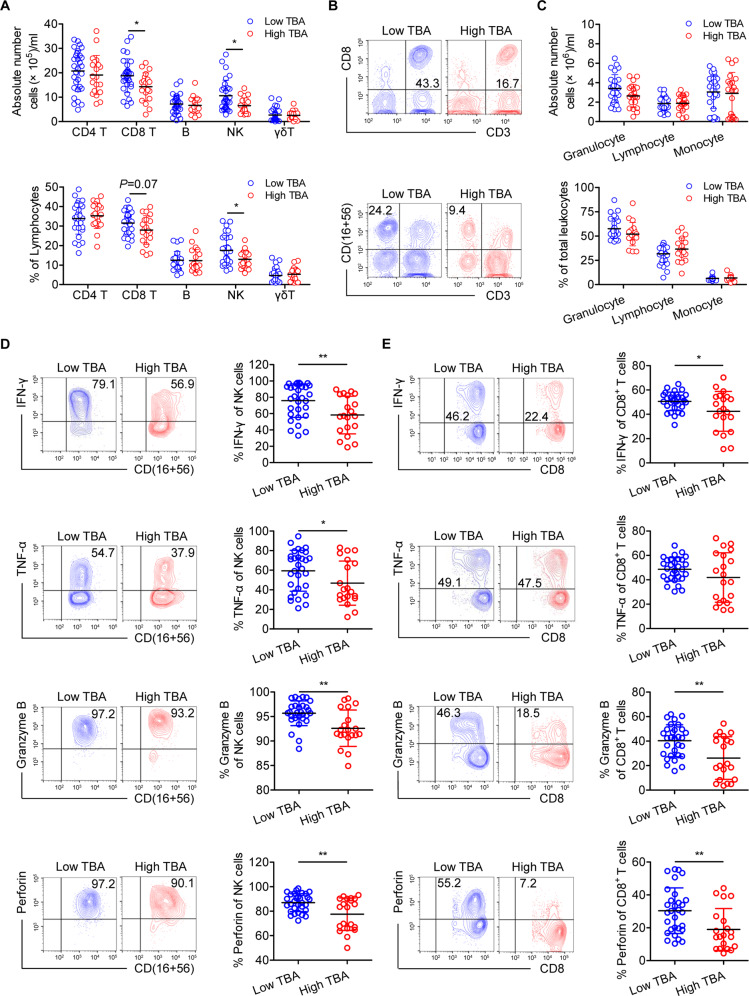
Fig. 3.
Bile acids impair the effector functions of CD3+CD8+ T and NK cells in HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B patients. A Quantification of CD3+CD4+ T cells, CD3+CD8+ T cells, B cells, NK cells, and γδ+ T cells in HBeAg-positive CHB patients with low (n = 30) or high (n = 20) TBA levels. The absolute number of immune cells was calculated by multiplying the total number of peripheral blood leukocytes by the percentage of positive cells. B Representative flow cytometry (FCM) profiles of CD3+CD8+ T and NK cells are shown for each group. C The number and proportion of granulocytes, lymphocytes, and monocytes within the total leukocyte population were determined by a hematology analyzer for HBeAg-positive CHB patients with low (n=30) or high (n=20) TBA levels. D, E Freshly isolated PBMCs from HBeAg-positive CHB patients with low (n=30) or high (n=20) TBA levels were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 5 h. Representative FCM profiles and quantification of the expression of the indicated molecules in NK cells (D) and CD3+CD8+ T cells (E). Unpaired t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001