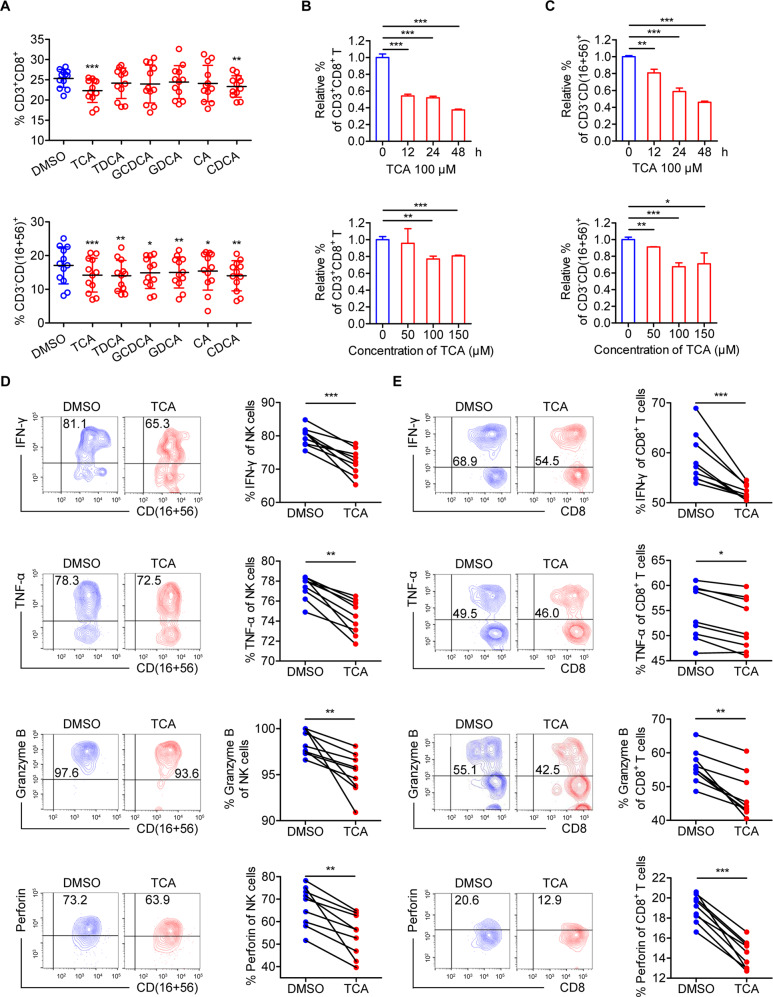
Fig. 4.
Taurocholic acid impairs the effector functions of CD3+CD8+ T and NK cells from patients with HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B in vitro. A Freshly isolated PBMCs from HBeAg-positive chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients (n = 12) were stimulated with or without a variety of BAs (100 μM). Cultured cells were harvested after 12 h and analyzed. The proportions of CD3+CD8+ T cells and NK cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Paired t test. B, C The relative proportions of CD3+CD8+ T cells (B) and NK cells (C) were analyzed by flow cytometry in freshly isolated PBMCs stimulated with 100-μM taurocholic acid (TCA) for the indicated times or stimulated with TCA at different concentrations for 24 h. Unpaired t test. D, E Freshly isolated PBMCs from CHB patients (n = 9) were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 5 h after stimulation with or without TCA (100 μM) for 24 h, and intracellular staining of IFN-γ, TNF-α, granzyme B, and perforin was determined using flow cytometry by gating on NK cells (D) and CD3+CD8+ T cells (E). Paired t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001