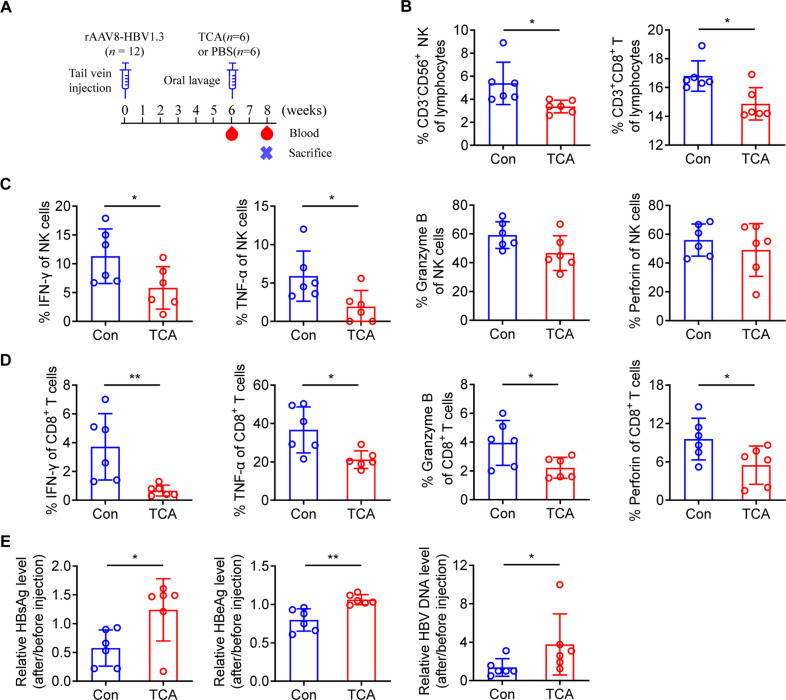
Fig. 5.
Taurocholic acid impairs the effector functions of CD3+CD8+ T and NK cells in vivo. A Schematic representation of HBV markers and immune cell detection. B After 2 weeks of taurocholic acid (TCA) administration (100 mg/kg/day), the proportions of NK and CD3+CD8+ T cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. C, D After 2 weeks of TCA administration, freshly isolated PBMCs from C57BL/6 mice were stimulated with PMA and ionomycin for 5 h, and then intracellular staining of IFN-γ, TNF-α, granzyme B, and perforin was determined using flow cytometry by gating on NK cells (C) and CD3+CD8+ T cells (D). E After 2 weeks of TCA administration, serum HBsAg, HBeAg, and HBV DNA levels were measured. Unpaired t test. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01