Fig. 7.
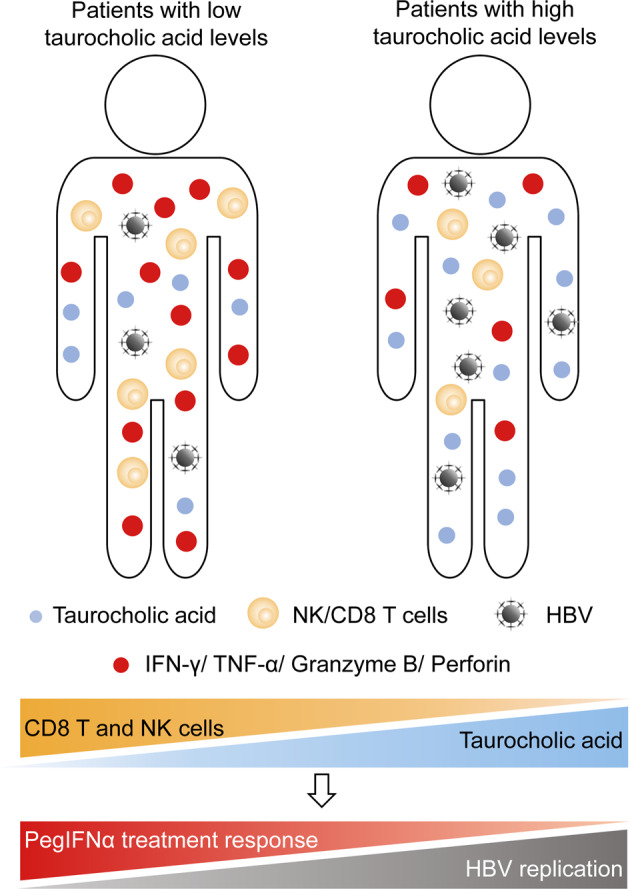
A model describing the mechanism regarding the inhibitory effect of taurocholic acid on the response to interferon-α therapy in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Compared with chronic hepatitis B (CHB) patients with low taurocholic acid (TCA) levels, CHB patients with high TCA levels had a lower number of CD3+CD8+ T and NK cells and lower levels of IFN-γ, TNF-α, granzyme B, and perforin secreted by CD3+CD8+ T and NK cells, resulting in the poor therapeutic response to pegylated interferon-alpha (PegIFNα) in CHB patients
