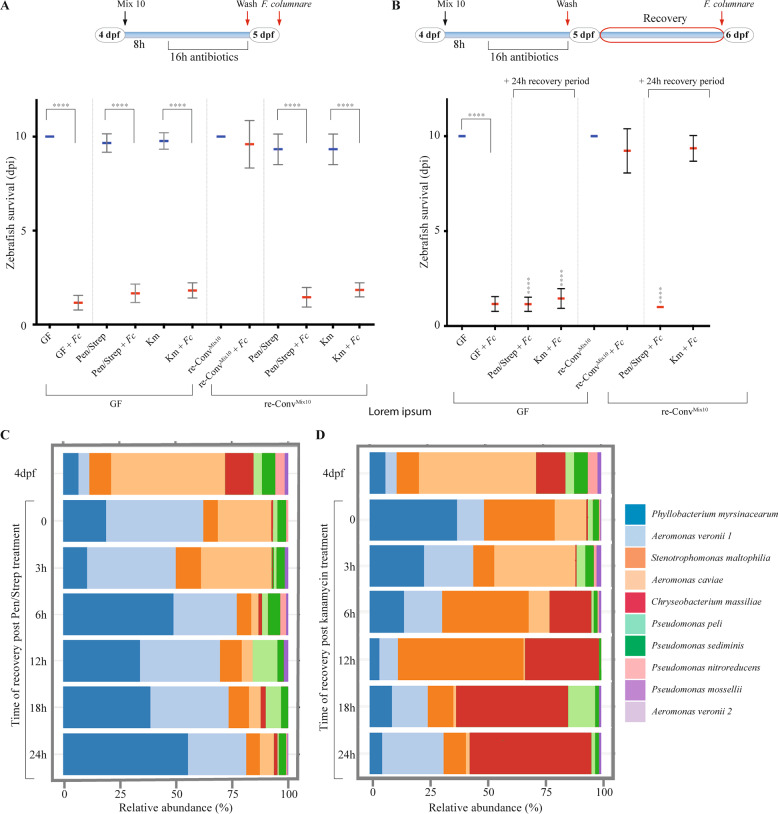
Fig. 2. Analysis of protection against F. columnare infection after antibiotic dysbiosis.
a Response of zebrafish larvae to exposure to F. columnareALG after antibiotic-induced dysbiosis with a diagram showing timing and treatments of the experiment. b A 24 h period after antibiotic treatment allows the recovery of protection in kanamycin-treated zebrafish larvae with a diagram showing timing and treatments. Mean survival is represented by a thick horizontal bar with standard deviation. For each condition, n = 12 zebrafish larvae. Blue mean bars correspond to larvae not exposed to the pathogen and red mean bars correspond to exposed larvae. Larvae mortality rate was monitored daily and surviving fish were euthanized at day 9 post exposition to the pathogen (9 dpi). Indicated statistics correspond to unpaired, nonparametric Mann–Whitney test. ****p < 0.0001; absence of *: non-significant. c Community recovery profile of re-ConvMix10 larvae with streptomycin/penicillin treatment. d Community recovery profile of re-ConvMix10 larvae with kanamycin treatment. Pools of 10 larvae were collected for 16S rRNA sequencing for both antibiotic treatments.