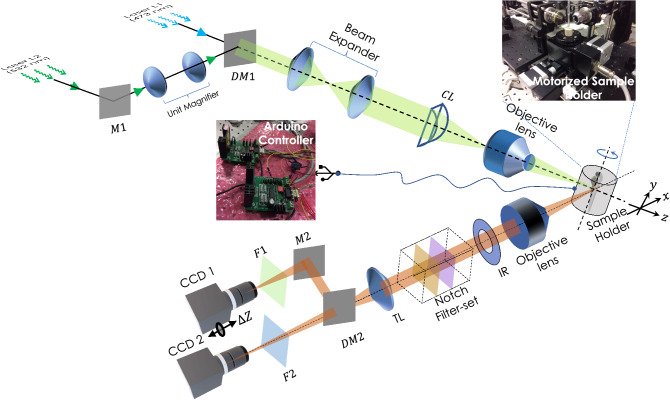
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of multicolor Lightsheet based OVSS fluorescence system. Two distinct wavelength of light sources ( nm and nm) are used to excite spectrally-distinct fluorophores. A unit magnifier (with lens separated by a distance ) is placed in one of the illumination arms to correct for the focal-shift () due to chromatic aberration induced by 10 objective lens. Beams are combined by Dichroic mirror (DM1), expanded and passed through cylindrical lens (CL, mm) to generate the light sheet. Additionally, we placed an objective lens (Olympus, 10, 0.3 NA) at the focus of cylindrical lens to generate diffraction-limited multicolor lightsheet (MLS). The specimen (encaged in a capillary tube) placed on the automated rotating-stage is illuminated by MLS. To observe the fluorescence, an orthogonal detection system is employed that use a separate detection objective lens (Olympus, 4X, 0.1 NA/Olympus, 10, 0.25 NA) to collect the image data. Iris (IR) and Notch filters (473 NF and 532 NF) are used to cut-off the nonparallel and scattered light respectively. Bandpass fluorescent filters (range nm) along with the dichroic mirror DM2 (with cut-off, nm), additional filters (F1 and F2), mirror (M2) and tube-lens (TL) are used to divert, filter and focus beam to the respective cameras ports (CCD1 and CCD2) for data recording.