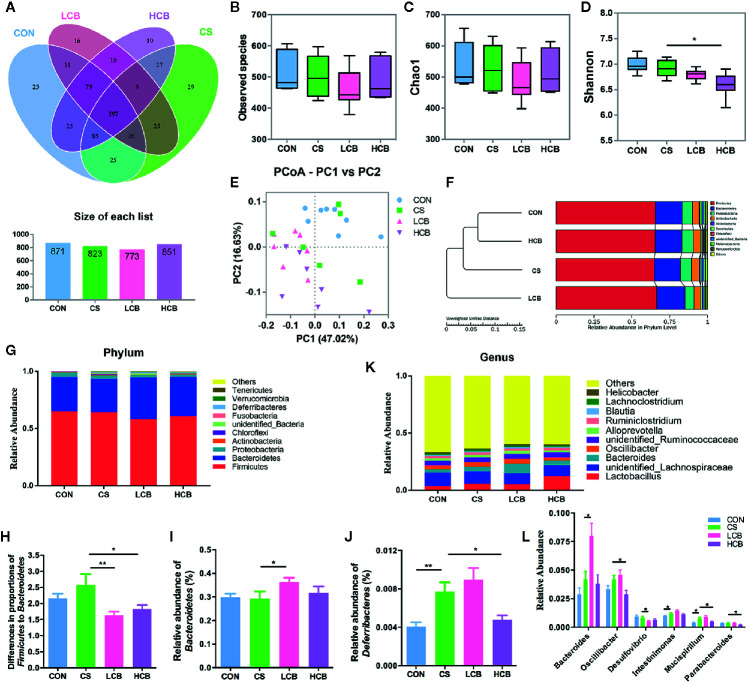
Figure 2.
Evaluation of illumina HiSeq sequencing data showing that CB RH2 could modulate the structure and composition of gut microbiota. (A) Venn diagram of shared and independent bacterial OTUs in different experimental groups (n >6); (B–D) Analysis of α-diversity of gut microbiota by Observed species, Chao1 and Shannon index; (E) Principal coordinate analysis (PCoA) based on weighted Unifrac distances among different samples. PC1 and PC2 account for 63.65% of the variation; (F) Multivariate analysis of variance from PCoA matrix scores using UPGMA method based on weighted Unifrac distances; (G) The average abundance of microbial community in different mice groups at phylum level; (H) The ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroidetes; (I, J) Statistical analysis for Bacteroidetes and Deferribacteres at the phylum level; (K) Bar charts at genus level of gut microbiota in the four groups; (L) Relative abundance of Bacteroides, Oscillibacter, Desulfovibrio, Mucispirillum and Parabacteroides are significantly manipulated by CB RH2 at genus level. Statistical analysis was performed using the t tests method. All values are mean ± SEM (n >6). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.