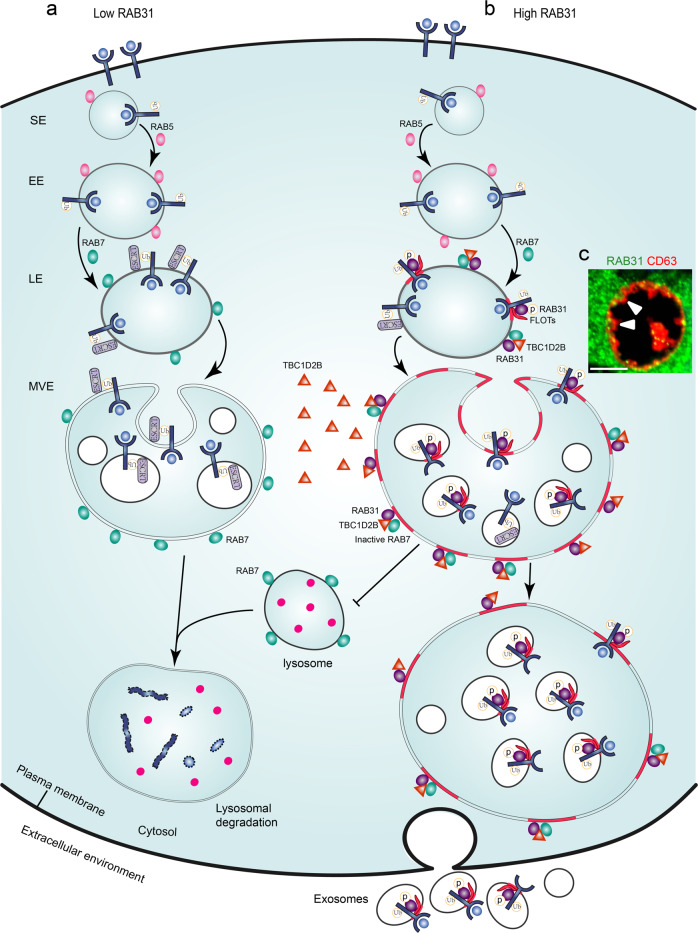
Fig. 9. The proposed model for the functions of RAB31 in exosome pathway.
EGFR are endocytosed into cells to form signaling endosomes (SE) and early endosomes (EE) regulated by RAB5, and then are transported from early to late endosomes (LE) regulated by transition from RAB5 to RAB7. a At this time, ESCRT machinery sorts the ubiquitylated EGFR into intraluminal vesicles (ILVs) that are destined to lysosomes for degradation by the fusion of multivesicular endosomes (MVEs) with lysosomes regulated by RAB7. b However, high RAB31, guarding on the late endosomes, encounters active EGFR and can be activated via tyrosine phosphorylation by EGFR, and then active RAB31 engages FLOTs in lipid rafts to drive EGFR entry into MVEs to form ILVs. Meanwhile, RAB31 recruits TBC1D2B to inactivate RAB7 preventing the fusion of MVEs with lysosomes, thereby enabling that the sequestered EGFR ILVs are secreted as exosomes. c Representative image of MVE membrane budding to form ILVs driven by the active RAB31 in NCI-H1975 cells. The white triangles indicate the budding moments of MVE membrane. Immunofluorescence of endogenous RAB31 (green) and CD63 (red) in NCI-H1975 cells. Scale bar, 5 μm.