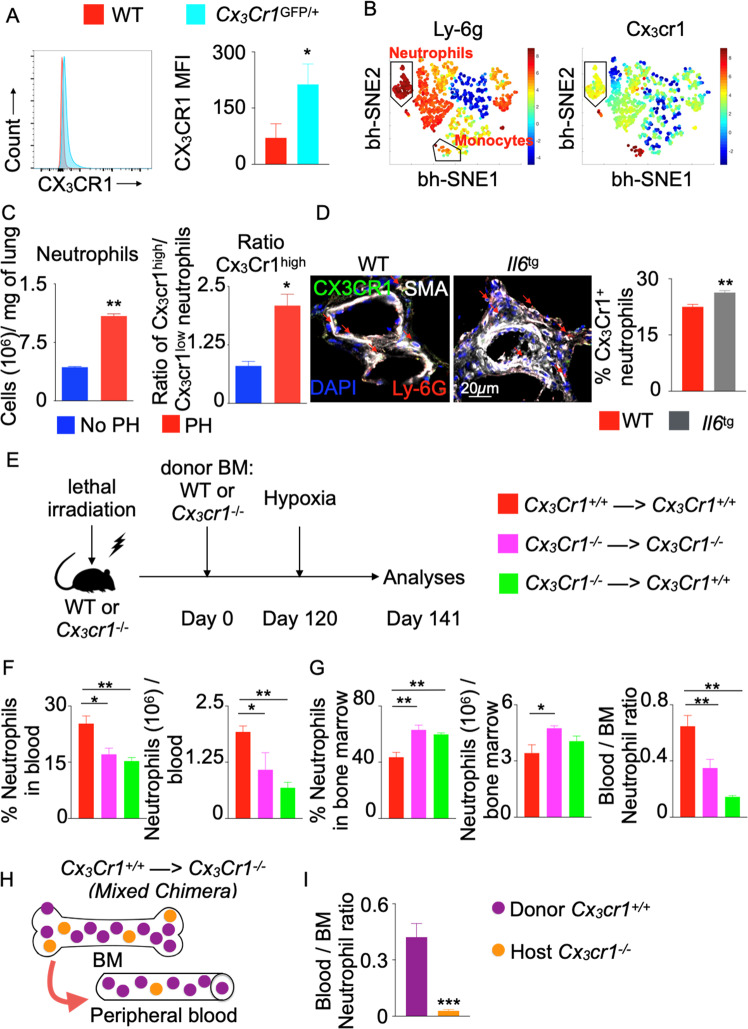
Fig. 4.
Neutrophils require CX3CR1 for egress from the bone marrow. Wild-type and Cx3cr1GFP/+ mice were placed in a hypoxic chamber for 3 weeks (n = 5 per group). The expression of Cx3cr1 in bone marrow neutrophils from these mice was evaluated by flow cytometry (A) and computational analyses (B). The left and right bh-SNE plots show the expression of Ly-6G and Cx3cr1 in bone marrow leukocytes, respectively. Total and Cx3cr1high neutrophils in the lungs of wild-type mice exposed to normoxia (No PH) or hypoxia (PH) were enumerated by flow cytometry (C) and wild-type and Il6 transgenic (Il6tg) mice exposed to hypoxia were examined using confocal microscopy (D). Arrows indicate Cx3cr1+ neutrophils. E Lethally irradiated Cx3cr1+/+ or Cx3cr1−/− mice were transplanted with bone marrow isolated from Cx3cr1+/+ or Cx3cr1−/− mice. Four months after transplantation, the chimeric mice were placed in hypoxic chambers for 3 weeks (10% O2) (n = 10 per group). The numbers and percentages of neutrophils among myeloid cells in the blood (F) and bone marrow (G) were assessed by flow cytometry. H Schematic showing the strategy to generate mixed bone marrow chimeras by transplanting Cx3cr1−/− mice with Cx3cr1+/+ bone marrow (n = 10 per group). I Bar graph showing the ratio of blood and bone marrow neutrophils of either donor or host origin. The data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005