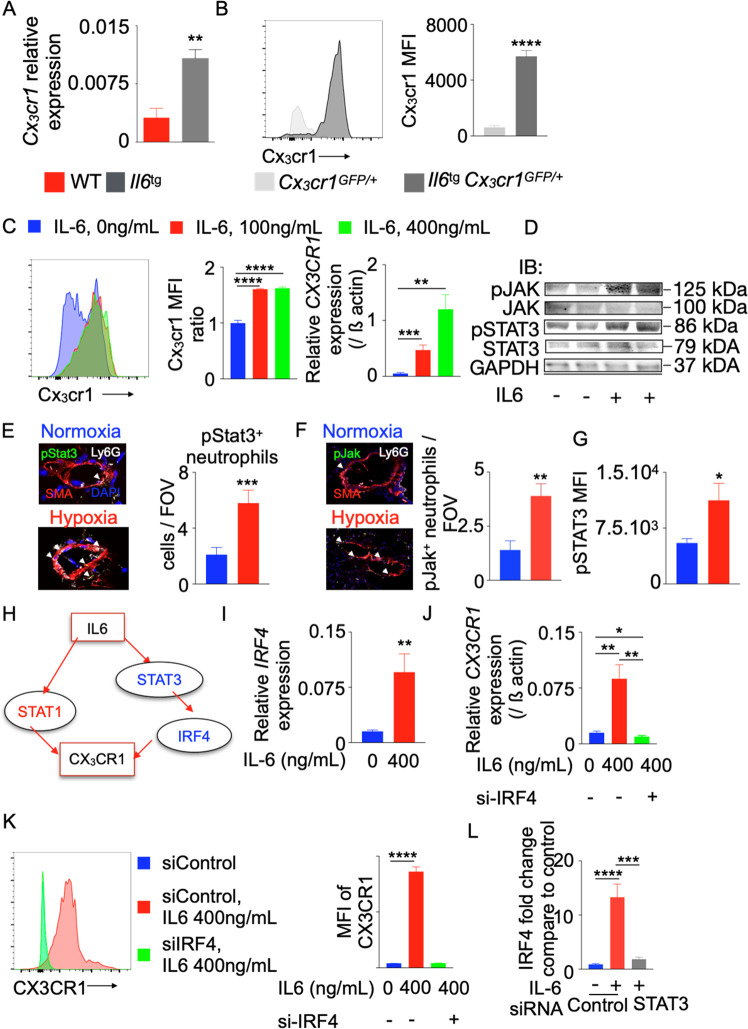
Fig. 5.
IL-6 increases CX3CR1 expression in neutrophils by increasing IRF4 expression. Il6-transgenic (Il6tg) and wild-type mice were placed in a hypoxic chamber (10% O2) (n = 5 per group) for 3 weeks to induce PH. A Relative Cx3cr1 expression in the lungs was quantified by RT-qPCR and standardized to beta actin expression. B Histogram and bar graph showing the expression of Cx3cr1 in wild-type and Il-6tg mice expressing GFP under the Cx3cr1 promoter. C Differentiated HL-60 cells were treated with various concentrations of recombinant IL-6 (0, 100, and 400 ng/mL). CX3CR1 expression was determined by RT-qPCR and flow cytometry (n = 5 per group). One of three representative experiments is shown. pSTAT3 and JAK levels in HL-60 cells treated with IL-6 (D) and neutrophils from the lungs of mice (E, F) and patients (G) with PH were quantified using immunoblotting and confocal microscopy. H Ingenuity pathway analysis (IPA) software was used to identify possible transcription factors that mediate IL-6-induced CX3CR1 expression. I, J Differentiated HL-60 cells were treated with recombinant IL6 (400 ng/mL) and control or IRF4 siRNA (n = 5 per group). A Representative experiment is shown. IRF4 expression was determined by RT-qPCR (I). CX3CR1 expression was determined by RT-qPCR (J) and flow cytometry (K). L Bar graph showing IRF4 expression in HL-60 cells treated with siControl or siSTAT3 and recombinant IL6. The data are shown as the mean ± s.e.m., *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.005; ****P < 0.001