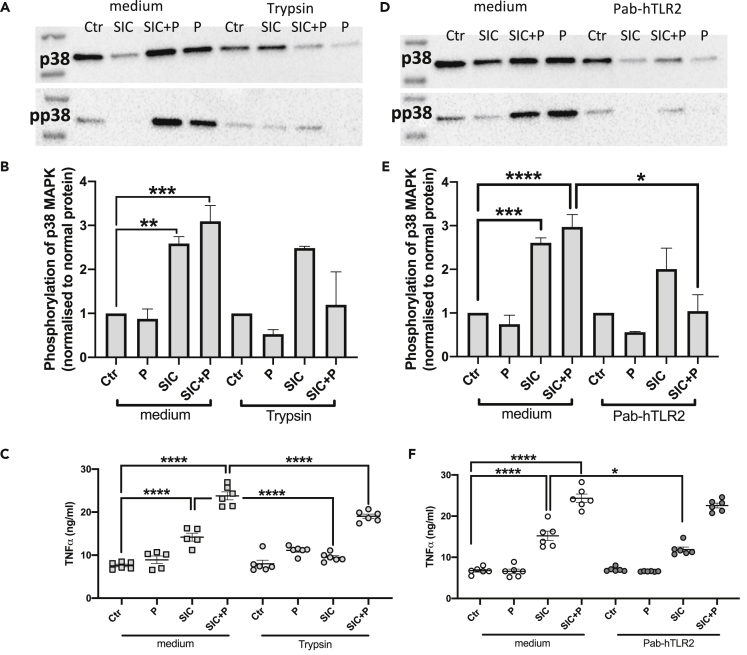
Figure 7.
SIC triggers p38 MAPK activation and TNFα release from primary CD14 + monocytes
(A) Western blot analyses of CD14+ cell lysates before and after trypsin treatment (100 μg/mL); cells were stimulated with 5 μg/mL SIC +/− 2.5% plasma (P). Membranes were incubated with antibodies against p38 MAPK (p38) and phosphorylated p38 MAPK (p-p38).
(B) Quantification of phosphorylation of Western blots of CD14+ monocytes treated with 100 μg/mL trypsin for 30 min. The band intensities of p-p38 samples were normalized to loading control (p38 band) and values analyzed.
(C) CD14+ cells were pre-incubated with 100 μg/mL trypsin, and then incubated with 5 μg/mL by SIC +/− 2.5% plasma (P). Absorbance was measured by ELISA at 450 nm.
(D) Western blot analyses of CD14+ cell lysates after stimulation with 5 μg/mL SIC +/− 2.5% plasma (P). Cells were pre-incubated with Pab-hTLR2 for 20 min. Membranes were incubated with antibodies against p38 MAPK (p38) and phosphorylated p38 MAPK (p-p38).
(E) Quantification of phosphorylation of Western blots of CD14+ cells treated with a neutralizing antibody against TLR2. The band intensities of p-p38 samples were normalized to loading control (p38 band) and values analyzed.
(F) CD14+ cells were pre-incubated with a neutralizing antibody against TLR2, and then incubated with 5 μg/mL SIC +/− 2.5% plasma (P). Release of TNF α was measured at 450 nm. All data represent mean ± SEM of 3-5 independent experiments, one-way ANOVA, Dunnett's multiple comparison test, with single pooled variance. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.001 ∗∗∗∗p < 0.0001.