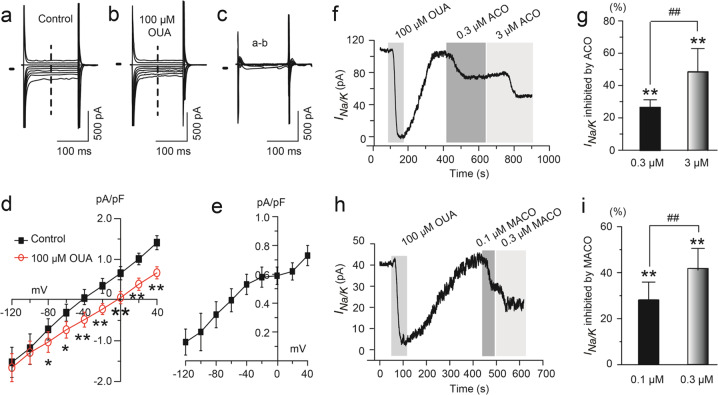
Fig. 7. Effects of ACO and MACO on the INa/K in guinea pig ventricular myocytes.
a–e The INa/K was determined to be an OUA-sensitive component in guinea pig ventricular myocytes. Superimposed current traces in response to 150-ms voltage steps to potential levels between +40 and −120 mV steps applied from a holding potential of 0 mV before (a) and 3 min after exposure to 100 μM OUA (b). OUA-sensitive difference currents at test potentials (between +40 and −120 mV) (c) were obtained by digital subtraction of the membrane current in the presence of OUA from that in its absence at each test potential. The zero-current level is indicated to the left of the current records by a horizontal line in (a), (b), and (c). d. I–V relationship analysis according to the membrane currents at 75 ms (dashed line as shown in (a) and (b) measured in the absence and presence of OUA. e The I–V relationship for the INa/K determined as an OUA-sensitive current was derived from the data subtraction of (d). f–i The INa/K was inhibited by ACO and MACO in a concentration-dependent manner. The time course of the INa/K in the presence of OUA, ACO, or MACO is shown in (f, h), the percentage inhibition of the INa/K by ACO at 0.3 and 3 μM is shown in (g), and the percentage inhibition of the INa/K by MACO at 0.1 and 0.3 μM is shown in (i). There were five cells from three guinea pig hearts in the ACO group and six cells from three guinea pig hearts in the MACO group. **P < 0.01, vs. control; ##P < 0.01, between treatments.