Fig. 8. Schematic diagram of the protective effect of SAA on vascular permeability via inhibition of VEGFA-Src-MMP signaling pathway activation during acute ischemic stroke.
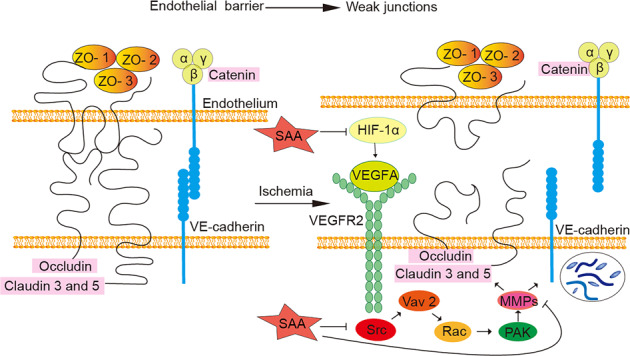
The endothelial barrier is maintained by the integrity of TJs and adherens junctions. During acute ischemic stroke, the expression of VEGFA increases obviously, and VEGFA binds to its receptor VEGFR-2. This receptor causes the sequential activation of VAV2-Tyr172, Rac, and PAK through Src. Activation of PAK increases the activity of MMPs, leading to VE-cadherin internalization and a subsequent increase in vascular permeability (VE-cadherin is an important factor in the formation of the vascular endothelial cell adhesion junction complex, which regulates the opening and closing of the endothelial barrier [23]). Upregulation of MMP protein expression also induces the degradation of TJ proteins. SAA protects the BBB by inhibiting the activation of the VEGFA-Src-MMP signaling pathway during acute ischemic stroke.
