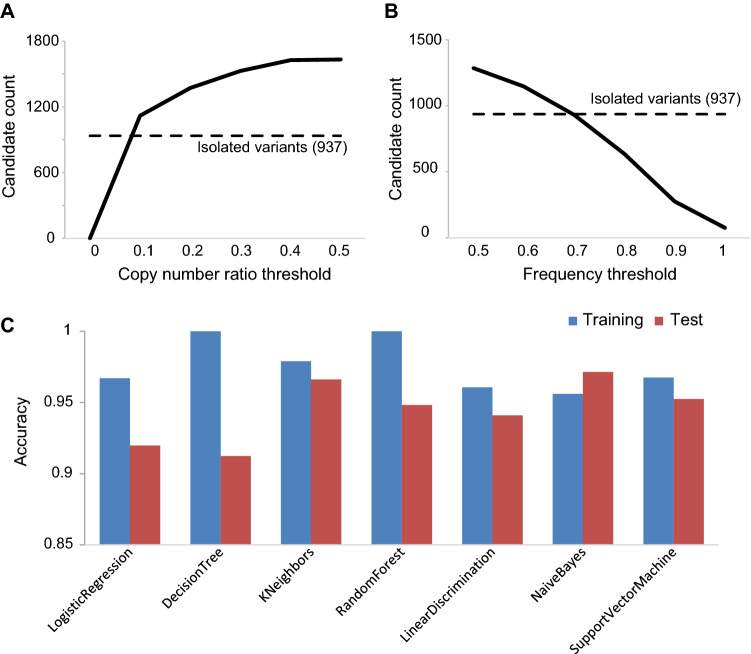
Figure 6.
Machine learning to filter false-positive candidates. (A,B) In the general copy number analysis of WGS data, the copy number ratio value (Supplementary Fig. S4) is used for indicator of deletions, and the frequency of a variant is used for the criterion whether it is homozygous or not. From the detected candidate variants, we counted the number of them with lower than a certain value of the normalized depth (A), and the number of them with higher than a certain value of the frequency (B). The broken line shows the number of isolated homozygous variants. (C) For the selection of variants by machine learning, we tested 7 algorithms, logistic regression (LR), decision tree (DT), k-nearest neighbor (kNN), random forest (RF), linear discrimination (LDA), naïve Bayes (NB), and support vector machine (SVM). We used the data listed in Supplementary Table S5 for the training and Table S9 for the test. After the training, we checked the accuracy of prediction whether the candidate is true or false using each learned model. The result of prediction to training data (blue bar) and test data (red bar) was shown. The analysis was performed using our original script (https://github.com/YujiSue/python/blob/master/DeletionFilter.ipynb).