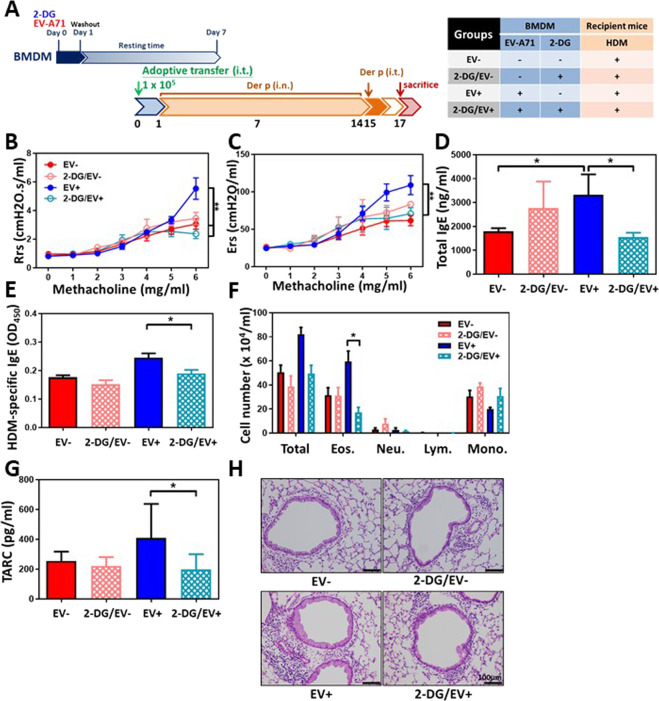
Fig. 6.
Adoptive transfer of EV-A71-trained BMDMs induces augmented airway allergic inflammation, which is blocked by pretreatment with 2-DG. A Protocol 3 experimental scheme. Mock-infected BMDMs (EV- group), 2-DG–treated mock-infected BMDMs (2-DG/EV- group), EV-A71–trained BMDMs (EV+ group) or 2-DG–treated EV-A71-trained BMDMs (2-DG/EV+ group) were intratracheally transferred into naïve mice. One day after adoptive transfer, allergic asthma was induced in these mice via intranasal and intratracheal challenge with HDM. B Airway resistance (Rrs) and C elastane (Ers) levels in response to increasing doses of aerosolized methacholine were measured using a flexiVent FX system (n = 6–8 mice, **p < 0.01, two-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni posttest). D Total IgE and E HDM-specific IgE serum concentrations were calculated using ELISA (n = 6–8 mice, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni multiple-comparison test). F Total cell, eosinophil, neutrophil, lymphocyte, and macrophage counts in the BALF were determined (n = 6–8 mice, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni multiple-comparison test). G TARC production in the BALF was evaluated using ELISA (n = 6–8 mice, *p < 0.05, one-way ANOVA with the Bonferroni multiple-comparison test). H Lung histology. Lung sections were stained with H&E (Scale bars = 100 μm). The findings represent pooled data from two independent experiments