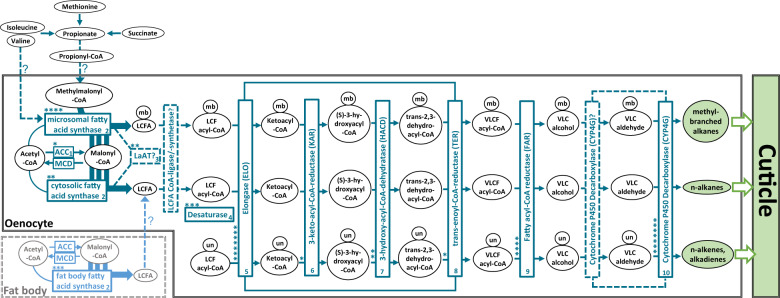
Fig. 2. Schematic summary of the current state of knowledge for the CHC biosynthesis pathway in insects.
Circles designate chemical compounds, rectangles the corresponding enzymes catalyzing their transitions. Enzymes are numbered from 1 to 10 according to their hypothesized order in the pathway, and asterisks correspond to the respective number of characterized genes whose depicted function has been empirically demonstrated through targeted knockdown studies listed in Table 1. Reactions and interactions in the CHC biosynthesis pathway that are not completely understood are marked with dashed arrows and question marks. Acetyl-CoA as the initial reactant of CHC biosynthesis is mainly provided by the citric acid cycle. Note that the distinction between microsomal and cytosolic fatty acid synthase is hypothetical and has not yet been unambiguously confirmed. Abbreviations: CoA: Coenzyme A, ACC: acetyl-CoA carboxylase, MCD: malonyl-CoA decarboxylase, LaAT: lipoamide acyltransferase, LCF(A): long-chain fatty (acid), VLC(F): very-long chain (fatty), mb: methyl-branched, un: unsaturated. Figure adapted and synthesized from Howard and Blomquist (2005), Blomquist and Bagnères (2010), Chung and Carroll (2015), Ginzel and Blomquist (2016).