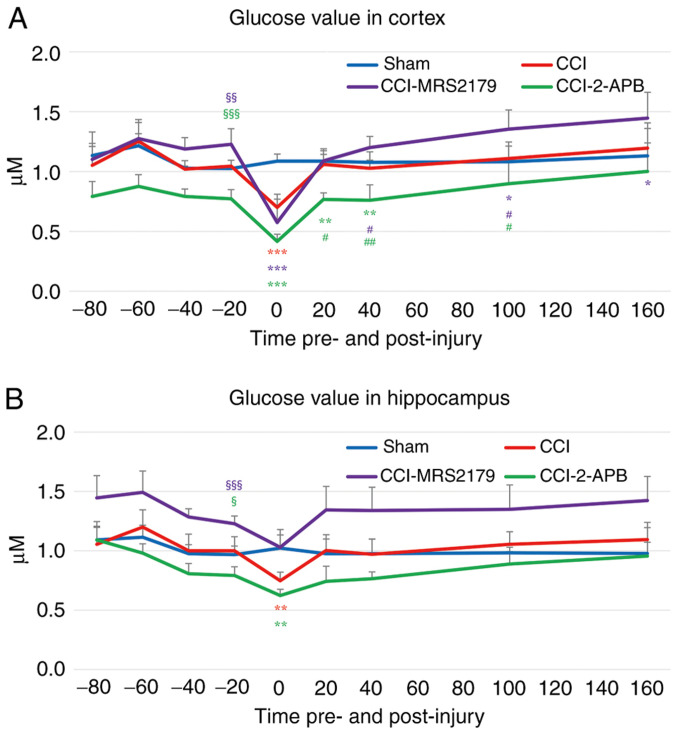
Figure 4.
Glucose levels in the extracellular space in the (A) cortex and (B) hippocampus. The times shown for each 20-min dialysate represent the start of each sample collection relative to the time of injury. Administration of MRS2179 increased, while administration of 2-APB decreased, the baseline (-20 min pre-injury) glucose levels in both brain regions compared with those of the sham group. The significant injury-induced decrease in glucose vs. the sham controls did not differ between the three CCI groups in the first post-injury dialysate sample from the cortex, although this decrease in the hippocampus did not reach significance in the CCI-MRS2179 group. Additional long-term reductions in extracellular glucose with 2-APB treatment and increases with MRS2179 treatment were also observed in the cortex. The color of each symbol denoting significant group differences correspond to the colors of the lines for each group shown in the legend. §P<0.05, §§P<0.01 and §§§P<0.001 vs. the sham group at -20 min pre-injury. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 and ***P<0.001 vs. the sham group post-injury. #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. the CCI group post-injury. 2-APB, 2-aminoethoxy diphenylborinate; CCI, Controlled cortical impact; MRS2179, MRS2179 ammonium salt hydrate.