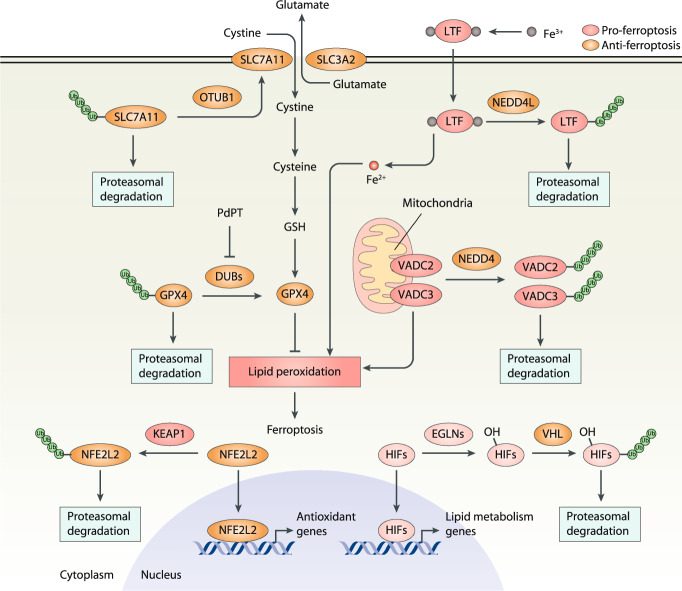
Fig. 3. Role of the ubiquitin-proteasome system in ferroptosis.
Lipid peroxidation is the core mechanism of ferroptosis, which is caused mainly by inhibiting the SLC7A11-GSH-GPX4 antioxidant pathway. The ubiquitin-proteasome system is involved in the degradation of SLC7A11, GPX4, LTF, VDAC2/VDAC3, NFE2L2, or HIFs during ferroptosis. DUBs deubiquitinases, EGLNs Egl-9 family hypoxia-inducible factors, GPX4 glutathione peroxidase 4, GSH glutathione, HIFs hypoxia-inducible factors, KEAP1 Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1, LTF lactotransferrin, NEDD4 NEDD4 E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, NEDD4L NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin protein ligase, NFE2L2 nuclear factor, erythroid 2-like 2, OTUB1 OTU deubiquitinase, ubiquitin aldehyde binding 1, SLC3A2 solute carrier family 3 member 2, SLC7A11 solute carrier family 7 member 11, Ub ubiquitin, VDAC2 voltage-dependent anion channel 2, VDAC3 voltage-dependent anion channel 3, VHL von Hippel–Lindau tumor suppressor.