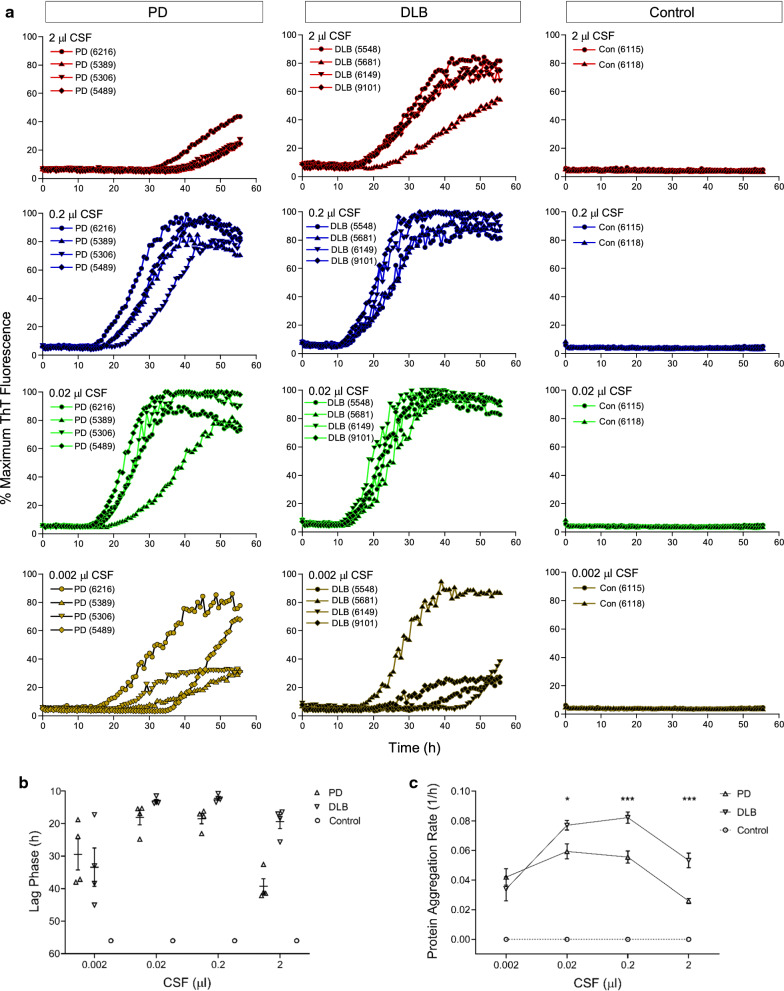
Fig. 2.
Ultrasensitive αSyn RT-QuIC assay of CSF samples of PD and DLB. a αSyn RT-QuIC spectra of postmortem CSF from neuropathologically confirmed cases of PD (n = 4, left panels), DLB (n = 4, middle panels), and NS controls (n = 2, right panels). Case numbers were indicated in parentheses. RT-QuIC reactions were seeded with 2 µl of CSF either undiluted or serially diluted to 10–1 through 10–3 (v/v), equivalent to 2–0.002 µl of original CSF. Average RT-QuIC reactivity was shown for individual CSF titrations in 4 cases of PD, 4 cases of DLB, and 2 cases of NS controls tested in quadruplicate. Data were expressed as percentages of the maximum ThT fluorescence. b Lag phase of RT-QuIC reactions seeded with individual CSF levels in PD, DLB, and control samples. RT-QuIC spectra for individual CSF levels of each case in a were used to obtain the time required for the average fluorescence to excess the threshold of RT-QuIC reactions (11% or 30,000 rfu). Shown were individual time points with error bars of means ± S.E. plotted against CSF levels. c Protein aggregation rate of RT-QuIC reactions seeded with individual CSF levels in PD, DLB, and control samples. Lag phase data (h) in b were converted to protein aggregation rate (1/h). Shown were average rate values and error bars of S.E. For negative reactions, the rate was set at 0 (dotted line). *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.005