Figure 5.
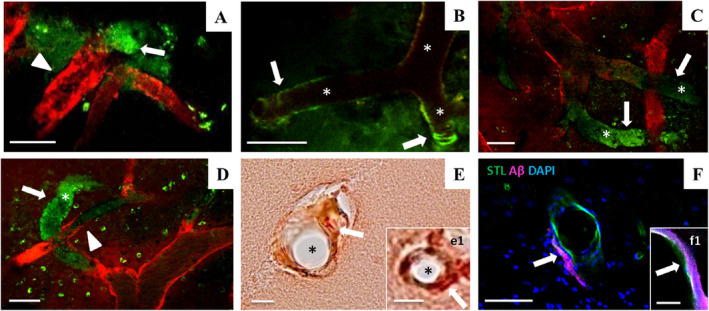
Intravital two‐photon microscopy of amyloid pathology in the parietal cortex of SHRSP. Vascular Methoxy‐positivity (green) indicative of CAA comprises periarteriolar or dysphoric CAA (A, arrow) and wall‐adherent amyloid deposits (arrows in B–D). CAA was detectable next to non‐occlusive erythrocyte thrombi (A and D, arrowheads) or surround totally obstructed vessel segments characterized by long distant Dextran gaps (asterisks in B–D) leading to the assignment of all Methoxy‐positive SHRSP to either HA stage 2 or stage 3. E and e1 (arrows) show CAA in the small vessel wall but no Aβ accumulation in the lumen of the vessel (asterisks in E and e1). STL (green in F and f1) marks the endothelium and therefore the inner layer of the vessel wall; the vascular amyloid deposits (magenta) are found in the second layer of the vessel wall called tunica media (F and f1). Data refer to the investigation of 13 male SHRSP aged 17–44 weeks. Small vessels and vessel walls are visualized by Dextran (red). CAA, cerebral amyloid angiopathy; HA, hypertensive arteriopathy. STL ‐ solanum tuberosum lectin (endothelial marker), DAPI ‐ 4′.6‐diamidino‐2‐phenylindole (nuclear staining); A–D—2PM, E and e1 ‐ CR/Prussian blue staining, F and f1—Immunohistochemistry; scale bars: A–D, F: = 50 μm, E = 20 μm, e1, f1 = 10 μm; age of the animals: A—28 weeks (w), B, E, F—32w, C–E—33w, e1 and f1 = 39w
