Figure 4.
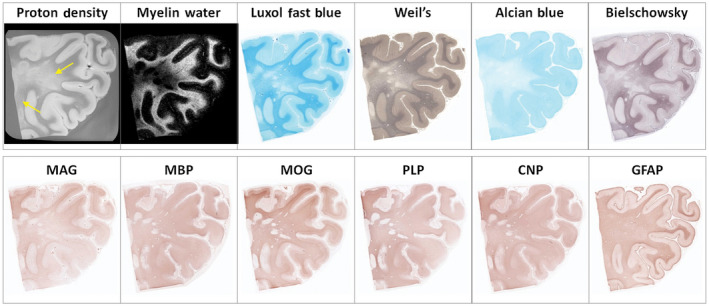
Example of diffusely abnormal white matter (DAWM) at 7T with corresponding myelin water map and histological stains for phospholipids (Luxol fast blue, Weil's), sialic acid groups (Alcian Blue), axons (Bielschowsky), myelin proteins (myelin‐associated glycoprotein (MAG), myelin basic protein (MBP), myelin oligodendrocyte protein (MOG), proteolipid protein (PLP), 2′,3′‐cyclic nucleotide 3′‐phosphohydrolase (CNP)), and astrocytes (GFAP). DAWM, characterized by an area of reduced intensity on the proton density (arrows) and myelin water map, matches a region of reduced staining intensity on the Luxol Fast Blue, Weil's, Alcian Blue, Bielschowsky, and, to a lesser degree, MAG stains. Several small plaques are seen within this region. Note the improvement in resolution in this high‐field strength compared to that at 1.5T shown in Figure 3. (Laule, C., Pavlova, V., Leung, E., Zhao, G., MacKay, A.L., Kozlowski, P., Traboulsee, A.L., Li, D.K., Moore, G.R.W. Diffusely abnormal white matter in multiple sclerosis: further histologic studies provide evidence for a primary lipid abnormality with neurodegeneration. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology 2013; 72( 1 ): 42–52, Figure 2 , by permission of Oxford University Press and the American Association of Neuropathologists)
