Figure 1.
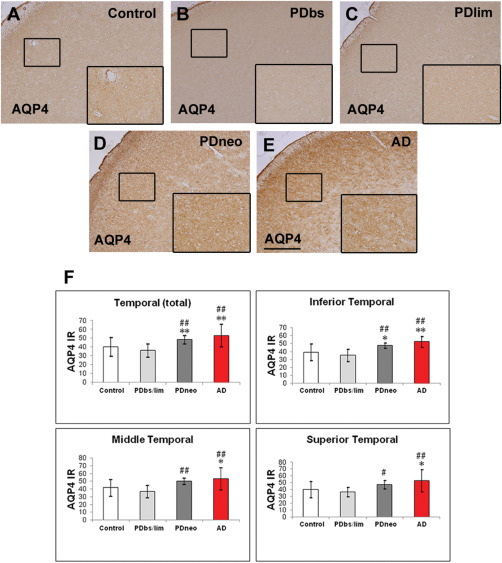
Immunohistochemistry for aquaporin 4 (AQP4) in the control brain (A), and brains with Parkinson's disease (PD) (B–D) and Alzheimer's disease (AD) (E).
PDbs, PDlim, and PDneo denote the brain stem, limbic, and neocortical groups, respectively. AQP4 immunoreactivity (IR) in the PDneo and AD groups is intense. Insets depict AQP4‐labeled areas (small squares). Scale bar: 500 μm. F: Intensity of the AQP4 IR in the total temporal neocortex (upper left panel) as well as in the inferior temporal cortex (upper right panel), in both the PDneo or AD groups is significantly greater than that in the control and PDbs/lim groups. The AQP4 IR in the middle and superior temporal cortex in the PDneo group is significantly greater than in the PDbs/lim group (lower panels). Data are given as mean ± SD. * P < 0.05 vs. control, ** P < 0.01 vs. control, # P < 0.05 vs. PDbs/lim, and ## P < 0.01 vs. PDbs/lim.
