Figure 6.
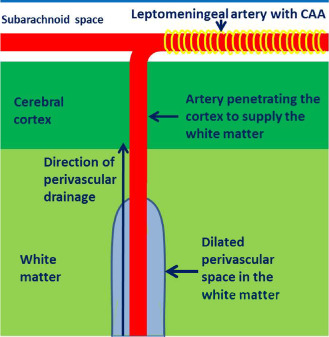
Proposed mechanism for CAA‐induced dilatation of perivascular spaces in the white matter. Branches of the leptomeningeal arteries penetrate the cortex (often without branching) to supply the subcortical white matter. CAA in the walls of the leptomeningeal arteries (yellow banding) obstructs the drainage of interstitial fluid and solutes resulting in retention of fluid in dilated perivascular spaces around arteries in the white matter.
