Figure 2.
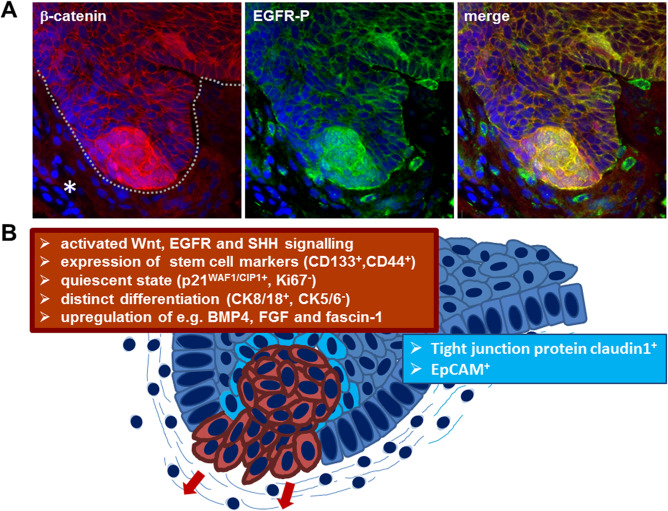
Subcellular characterization of ACP based on immunohistochemistry. Double immunohistochemistry (A) showing budding ACP tumor (line) into adjacent brain tissue (asterisk) with beta‐catenin accumulating cell clusters (red) at the tip of the finger‐shaped tumor protrusion. Detection of activated EGFR (EGFR‐P, green) reveals co‐localization within the beta‐ catenin accumulating cells (yellow) in the merged view, demonstrating co‐activation of Wnt signaling and EGFR signaling pathway within the same cells at the invasion front. Solid ACP areas reveal a different marker expression (B). The beta‐catenin accumulating cells are marked in red with the corresponding marker profile summarized in the red box. Cells surrounding the mostly whirl‐shaped beta‐catenin enriched cells (light blue) express enhanced levels of claudin‐1, involved in tight junction formation and the epithelial cell adhesion molecule EpCAM.
