Figure 1.
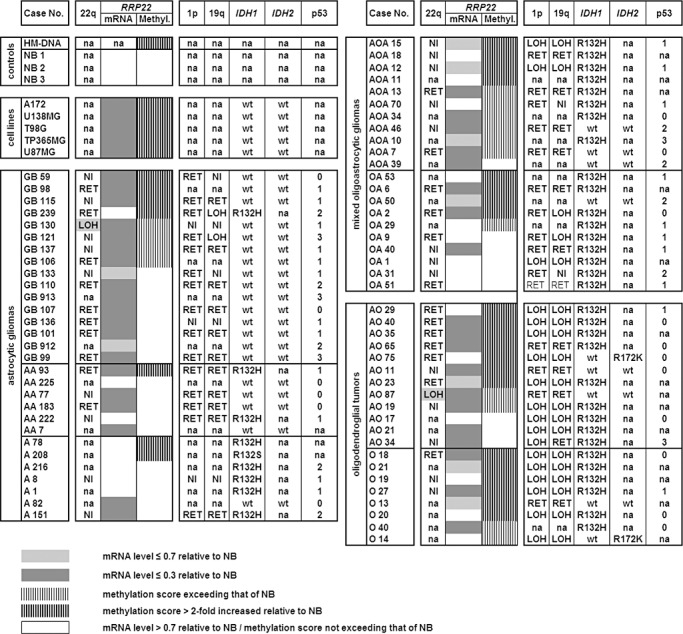
Molecular genetic aberrations of RRP22 in synopsis with other common molecular alterations in human gliomas. Note that RRP22 transcript levels (mRNA) are decreased relative to non‐neoplastic brain tissue in all glioblastoma cell lines and the majority of the investigated tumors. Transcriptional downregulation of RRP22 is only, in part, explained by RRP22 5'‐CpG island hypermethylation (methyl.). NB1‐3, 3 different samples of non‐neoplastic brain tissue; HM‐DNA, in vitro hypermethylated DNA control; LOH, loss of heterozygosity on 22q12 (spanning the RRP22 locus), 1p and 19q as assessed by microsatellite analyses; RET, retention of heterozygosity at all investigated informative loci on these chromosomal arms; NI, not informative at the investigated loci; na, not analyzed. IDH1/2 mutations were assessed by pyrosequencing (wt, wild‐type sequence) and p53 protein expression by semiquantitative immunohistochemistry (0, no immunopositive tumor cells; 1, <10%; 2, 10%–49%; 3, 50%–90% and 4, >90% tumor cells with immunopositive nuclei).
