Figure 1.
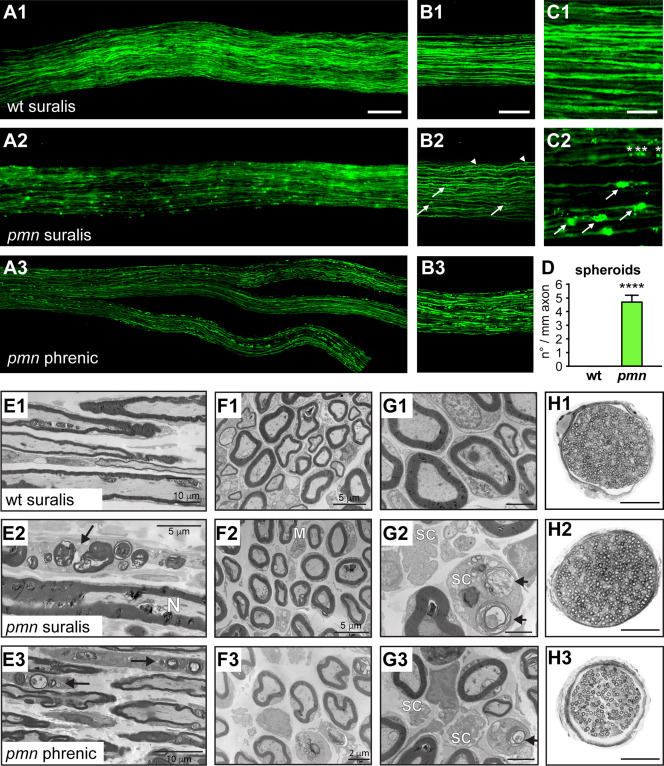
Sensory axon degeneration in suralis nerves of pmn mice revealed by axonal YFP imaging and electron microscopy. A. Images of suralis nerves from 25‐day old wildtype (wt) thy1‐YFP‐16 mice (A1) and pmn thy1‐YFP‐16 mice (A2) expressing YFP in axons. A pmn phrenic motor nerve with its distal branches (A3) is shown for comparison. Scale: 100 µm. B. Images of confocal z‐stacks showing axon caliber irregularities and axonal spheroids in peripheral nerves of pmn YFP mice (B2) as compared to wt (B1). In suralis nerves of pmn YFP mice, axonal spheroids occur in both large caliber axons (arrows) and small caliber axons (arrowheads). Signs of axon degeneration in suralis sensory axons are qualitatively similar to those in phrenic motor axons (B3) of pmn YFP mice but quantitatively less pronounced. Scale: 100 μm. C. High power microscopic images showing axonal spheroids in axons of pmn YFP suralis nerves (C2, arrows) but not in corresponding wt YFP axons (C1). Also note the presence of multiple small axonal YFP foci (asterisks) in the same axon. Scale: 30 μm. D. Quantitation of YFP spheroids in pmn suralis nerves. The number of spheroids per axon segment is about 100 fold higher in pmn YFP axons (4.69 ± 0.47) than in wt YFP axons (0.047 ± 0.013). Axons were monitored on single confocal sections and traced along > 200 μm length in z‐stacks of 20–30 μm depth. Number of axon blebs per mm axon segment is represented as mean of means per nerve ± sd. A total of 2701 axons (wt YFP: 203 to 427 per nerve, pmn YFP: 112 to 278 per nerve) was analyzed in five nerves per genotype. Statistical significance ****, P < 1.7 × 10−23 by Student's t‐test, unpaired, unequal variance. E. Electron microscopy images of longitudinal nerve sections. In comparison to the wt suralis nerve (E1), the pmn suralis nerve (E2) presents some damaged myelinated axons. These myelinated fibers are now a row of several aligned ovoids, consisting of myelin debris and disrupted axons (arrow). N: normal axon. Similar lesions are seen in the pmn phrenic motor nerve where two Schwann cells contain numerous myelin and axonal debris (ovoids, arrows) (E3). Scale bars see images. F. Electron microscopy of transverse sections. The density of myelinated axons is similar in wt (F1) and pmn (F2) suralis nerves. A macrophage (M) in the pmn suralis nerve is loaded with some myelin debris. Macrophages have only a plasma membrane but no basal membrane and present elongated cytoplasmic expansions. Schwann cells have a plasma and a basal membrane, and no elongated cytoplasmic expansions. Scale bars see images. G. High power electron microscopy images of transverse sections. In the pmn suralis nerve (G2) note myelin and axonal debris inside a Schwann cell (SC) cytoplasm (ovoid, arrow) and disappearance of unmyelinated fibers in the other Schwann cell. Ovoids are also seen in the pmn phrenic nerve (G3, arrow). Scale: 2 μm. H. Entire nerve cross sections (semi‐thin sections) show normal number of myelinated fibers in pmn (H2) as compared to wt suralis nerves (H1). Note severe degeneration of myelinated fibers in the pmn phrenic motor nerve (H3). Scale: 50 μm.
