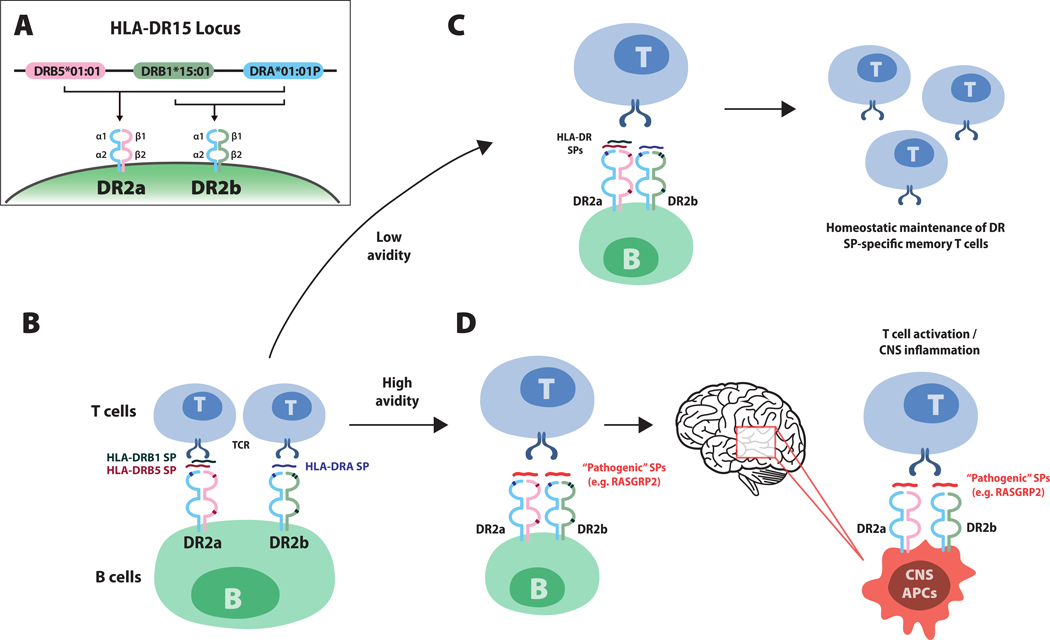
Figure I.
Model illustrating how human leukocyte antigen (HLA)-DR15-associated self peptides (SPs) on B cells influence the autoreactive T cell repertoire in multiple sclerosis (MS). Panel A shows the MS-associated HLA-DR15 locus. HLA-D proteins, which include three isotypes (-DQ, -DP and -DR), are major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules composed of alpha chain and beta chain heterodimers. MHC class II molecules, which are expressed antigen-presenting cells (e.g. B cells, monocytes and central nervous system [CNS] microglia), are required for the presentation of processed peptide fragments of foreign antigens or autoantigens to CD4+ T cells. The DR15 haplotype contains one alpha chain gene, DRA*01:01P, and two beta chain genes, DRB5*01:01 and DRB1*15:01 (Panel A). Pairing of the alpha chain with the beta chain encoded by DRB5*01:01 or the beta chain encoded by DRB1*15:01, respectively creates DR2a and DR2b heterodimers. A recent study by Wang et al.8 showed that small peptide fragments derived from DR2a and DR2b proteins themselves bind intact DR2a and DR2b molecules on B cells and serve as antigens for presentation to T cells (Panel B). Small peptides derived from the beta chains DRB5 (red) and DRB1 (green), bind to DR2a and small peptides from the alpha chain, DRA (blue), bound to DR2b. Panel C shows that HLA small peptides, which represent a large proportion of peptides binding DR2a and DR2b molecules on peripheral memory B cells in patients with multiple sclerosis, exhibit low avidity T cell receptor (TCR) engagement, supporting homeostatic (non-pathogenic) maintenance of HLA DR small peptide–specific memory T cells. Panel D shows how pathogenic small peptides, for example, peptides derived from RASGRP2, which is expressed by both B cells and neurons in the cortical gray matter, may replace DR2a and DR2b small peptides, leading to high avidity TCR engagement that would then promote the activation of pathogenic-peptide CD4+ T cells, which then traffic to the CNS. Antigen-presenting cells in the CNS that express DR2a and DR2b may present the corresponding pathogenic peptide expressed in the CNS (for example, RASGRP2) to CD4+ T cells, eliciting inflammatory responses and tissue damage.