Figure 3.
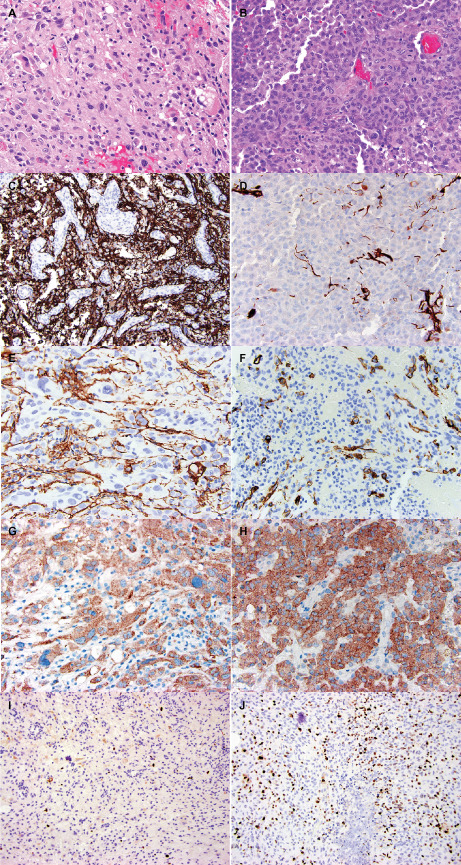
Comparison of morphologic and immunohistochemical features of PXA (left) and epithelioid (right) areas in a single case of ePXA (case 5). A. Illustrates an area composed of spindled and oval cells with irregular nuclear contours and variably vacuolated (lipidized) cytoplasm. Eosinophilic granular bodies and occasional bizarre, large cells are also seen. B. Shows the epithelioid regions of anaplastic transformation. The PXA areas were extensively positive for GFAP (cytoplasmic and fibrillary pattern) (C), whereas the epithelioid areas showed mostly loss of GFAP expression (D). Occasional tumor cells in the PXA areas demonstrated CD34 expression in an arborescent pattern (E). The epithelioid areas also contained occasional CD34‐positive tumor cells (F). Both areas demonstrated BRAF V600E mutant protein expression (G,H). The Ki67 immunostain revealed a low proliferation index in the PXA areas (I), and a considerably higher labeling index in the epithelioid areas (J).
