Figure 2.
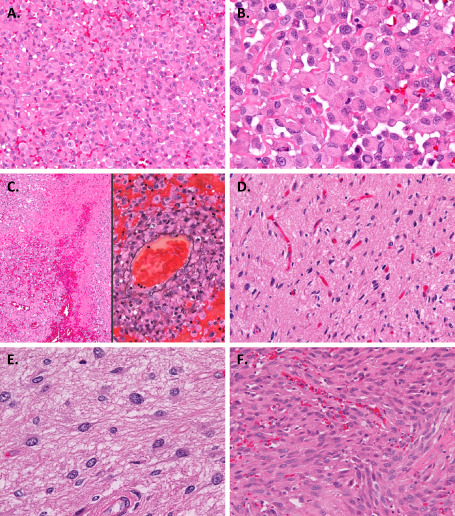
Microscopic appearance. A. The tumor was composed mainly of discohesive sheets of medium‐sized uniform cells. B. The tumor cells had rounded cytoplasmic contours and eosinophilic cytoplasm. The nuclei were large and mostly eccentric, and variable in shape: round, ovoid, reniform, crescent or ring‐like. The cells often had hyalinized cytoplasmic inclusions, some of which contained fine basophilic granules. C. Hemorrhage and coagulative necrosis (left). Tumor‐cell invasion into the vascular wall demonstrated by staining with both hematoxylin and eosin and periodic acid‐methenamine silver (right). D, E. A small area of the tumor displayed the proliferation of well‐differentiated neoplastic fibrillary astrocytes. F. A small part of the tumor extending within the subarachnoid space showed spindle‐shaped cells. Original magnification: ×100 (C left), ×200 (A, C right, D, F), ×400 (B, E).
