FIGURE 2.
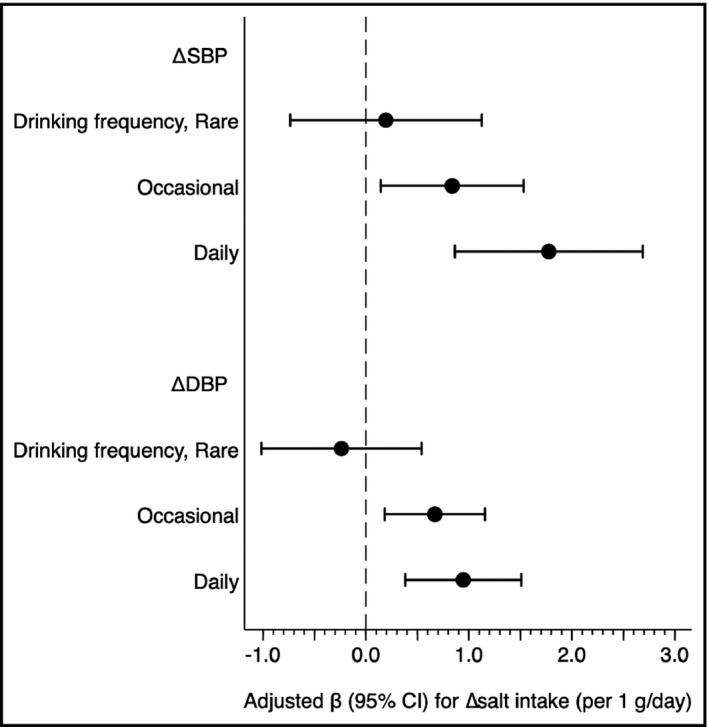
Drinking frequency modifies an association of the change of salt intake (Δ salt intake) with the change of systolic and diastolic blood pressure (∆SBP and ∆DBP). Adjusted β value were calculated using a linear regression model adjusting for age (y), sex, smoking status (non‐, past, vs current smoking), current treatment for dyslipidemia and diabetes, body mass index (kg/m2), SBP (if ΔSBP) (mm Hg), DBP (if ΔDBP) (mm Hg), total cholesterol (mg/dL), triglyceride (log mg/dL), hemoglobin A1c (%), estimated glomerular filtration rate (mL/min/1.73 m2), and salt intake (g/d) at the baseline visit
