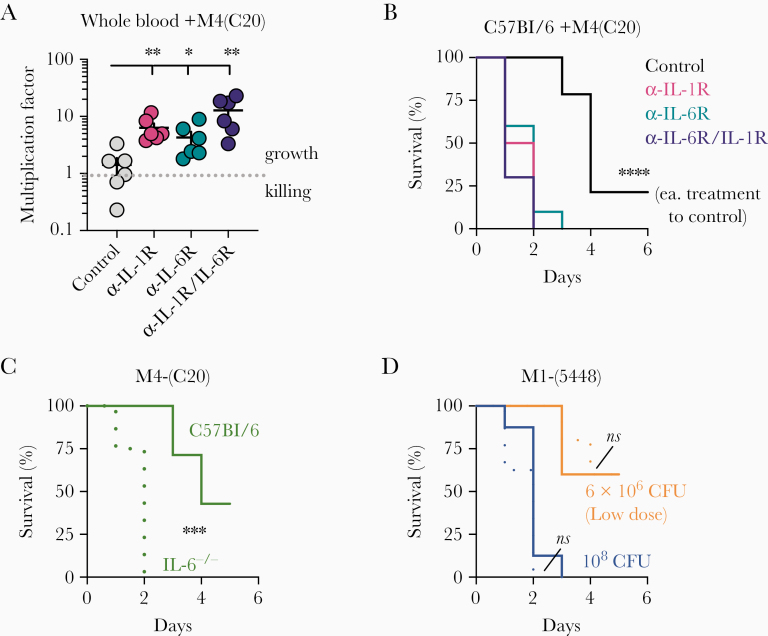
Figure 1.
Impaired interleukin 6 (IL-6) signaling promotes growth of group A Streptococcus (GAS) M4(C20). A, Heparinized whole human blood was treated with Kineret (α-IL-1R through rIL-1RA; 50 μg/mL) and/or tocilizumab (α-IL-6R neutralizing antibody; 50 μg/mL) with isotype antibody control (50 μg/mL) was inoculated with 107 colony-forming units (CFUs) of GAS M4(C20). After 24 hours, CFUs were enumerated for each group and growth determined relative to starting inoculum (multiplication factor); values >1 denote growth. Statistical significance between groups (n = 6) was determined by 1-way analysis of variance using Dunnett multiple comparisons analysis, using the immunoglobulin G (IgG) control group as the reference. Data are representative of 3 independent donors. B, Wild-type C57BL/6 mice were treated with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody against either IL-1R (red; n = 8), IL-6 (blue; n = 8), both (purple; n = 8), or an IgG (black; n = 8) isotype, then inoculated intravenously with 108 CFUs of GAS strain M4(C20) and monitored for the given time intervals. Statistics were calculated by log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test in comparison to control mouse group. C and D, C57BL/6 wild-type (solid lines) or IL6-knockout (IL6-/-; dotted lines) mice were inoculated intravenously with 108 CFUs of GAS strain M4(C20) (clinical isolate, green), 108 CFUs M1(5448) (blue), or 6 × 106 CFUs M1(5448) (orange; lower dose to more closely match M4(C20) kinetics) and monitored for the given time intervals. Statistics were calculated by log-rank (Mantel–Cox) test. Data represent at least 2 independent experiments with 8 mice each. *P < .05; **P < .005; ***P < .0005; ****P < .00005; ns, not significant.