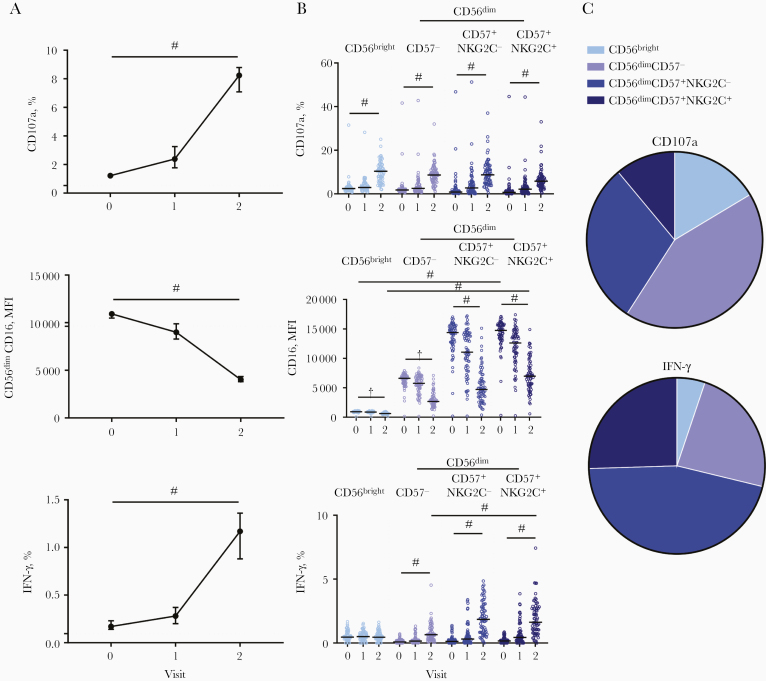
Figure 2.
Antibody-dependent natural killer (NK) cell responses to plate-bound Ebola virus glycoprotein after adenovirus type 26.ZEBOV, modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA)–BN-Filo vaccination. The median and 95% confidence interval of NK cell CD107a, CD56dimCD16 mean fluorescence intensity (MFI), and interferon (IFN) γ responses to prevaccination (visit 0), post–dose 1 (visit 1) and post–dose 2 (visit 2) vaccination serum sample are shown. A, All vaccine arms combined (n = 72). NK cell CD107a, CD16, and IFN-γ responses were analyzed according to NK cell differentiation subset, defined by CD56, CD57, and NKG2C expression (gating strategy shown in Supplementary Figure 1C). B, Each individual serum donor is represented by a dot with a line at the median. The proportion of total NK cell CD107a and IFN-γ expression (after dose 2) attributed to each subset is shown as a pie graph, with each slice representing the median. C, Comparisons across vaccination visits and between subsets were performed using 1-way analysis of variance with Holm-Sidak test for multiple comparisons. ‡P < .001.