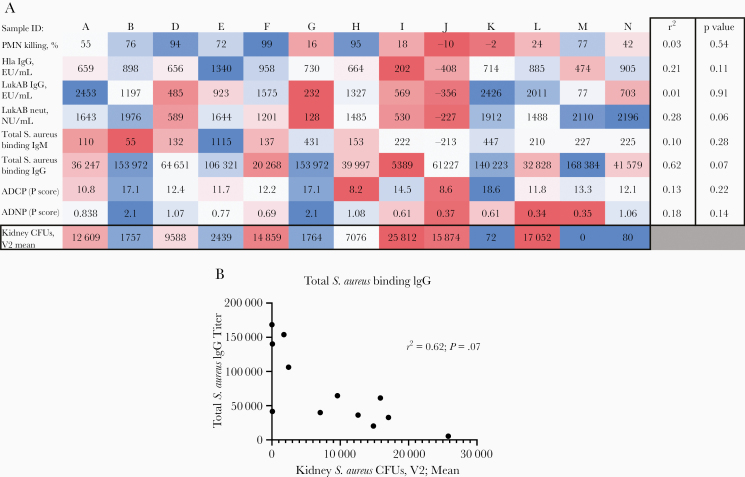
Figure 5.
Correlation of in vitro characteristics of human serum samples compared with efficacy of serum samples to protect against Staphylococcus aureus sepsis in mice after adoptive transfer. A, Correlation matrix with Pearson correlation coefficient of specific in vitro characteristics: facilitation of neutrophil-mediated killing; antiβα-hemolysin (Hla) immunoglobulin (Ig) G; anti-LukAB IgG; neutralization of LukAB-mediated phagocyte killing (neut); total S. aureus binding IgM and IgG by normalized enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay units (EU) per milliliter, antibody-dependent cellular phagocytosis (ADCP), and neutrophil phagocytosis (ADNP) (by phagocyte [P] score) compared with S. aureus colony-forming units (CFUs) in mice after adoptive transfer. Blue color on heat map indicates higher titer/improved function. After correction for multiple comparisons, the closest correlation was seen with total binding IgG against S. aureus (r2 = 0.62, suggesting strong correlation; P = .07). B, Correlation of total binding S. aureus IgG and mean CFU counts (n = 5 mice per group) for individual serum samples. CFUs were enumerated from whole homogenized organ in 1 mL of phosphate-buffered saline. Abbreviations: NU, neutralization units; PMNs, polymorphonuclear leukocytes; V2, 4–6 weeks after enrollment.