Figure 4.
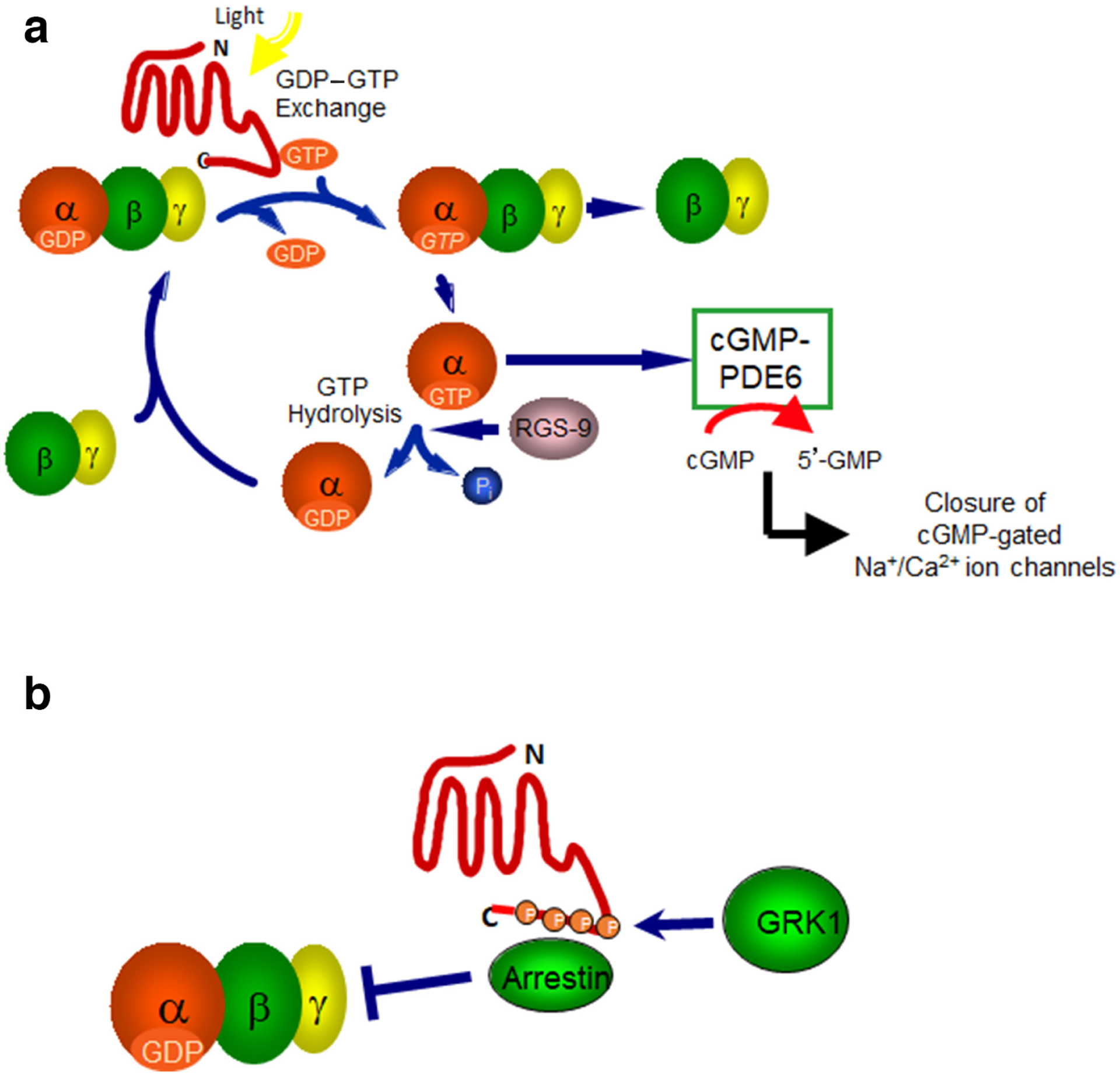
(a) Activation of rhodopsin by light stimulates transducin (Gt1) activation via guanine nucleotide exchange. The GTP-bound α subunit activates phosphodiesterase 6 (PDE6), which hydrolyses cGMP to 5′-GMP, thereby reducing cGMP levels and leading to the closure of the cGMP-gated Na+/Ca2+ ion channels. Inactivation of Gαt1-GTP occurs through hydrolysis of GTP to GDP promoted by the protein, Regulator of G protein Signalling 9 (RGS9). Gαt reassociates with βγ to form the inactive heterotrimeric G protein. (b) Inhibition of G protein signalling occurs through phosphorylation of the carboxyl terminus of rhodopsin by GRK1, followed by the binding of arrestin. Arrestin sterically blocks the binding of Gt.
