Figure 11.
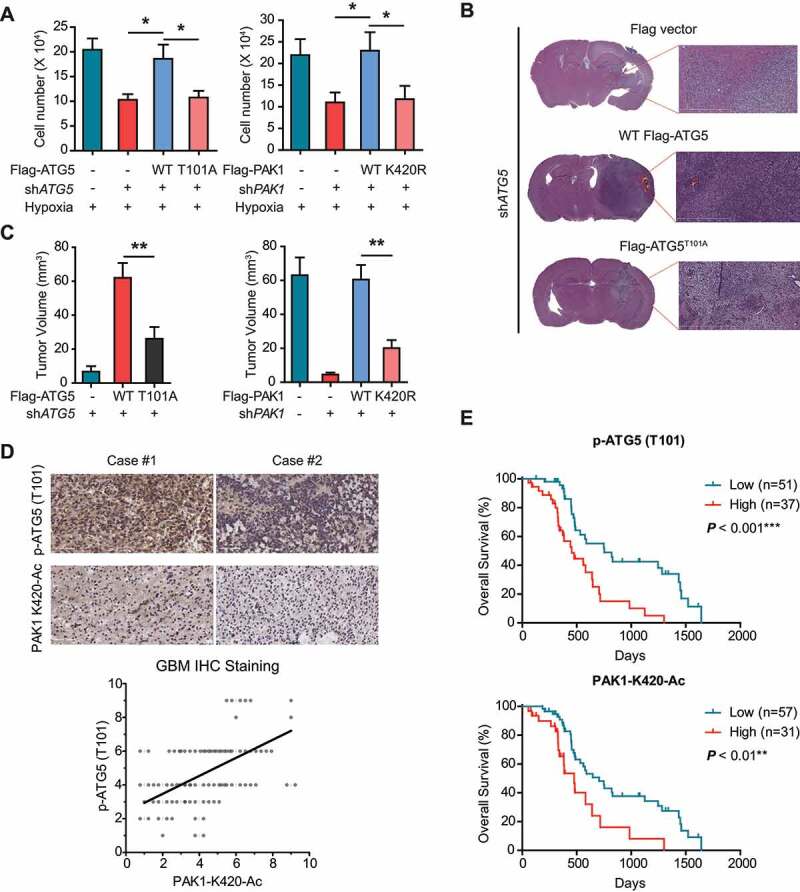
PAK1-mediated ATG5 phosphorylation at T101 promotes GBM development and relates to a poor prognosis. (A) The effects of PAK1 or ATG5 knockdown and reconstituted expression of the indicated plasmids on the proliferation of LN229 cells cultured in hypoxia condition for 3 d using MTT assay. (B and C) The effects of PAK1 or ATG5 knockdown with or without reintroduction of indicated plasmids on GBM growth after LN229 cells were injected into intracranially nude mice (n = 10 per group). And representative images (scale bar, 100 μm) of H&E and tumor volumes were shown. (D) IHC staining of human GBM samples. Scatterplot depicting the indicated levels of PAK1-K420-Ac and p-ATG5 (T101) protein in human GBM (n = 88) by IHC (bottom). Pearson’s correlation coefficient was determined. (E) GBM patients were stratified by ATG5 (T101) phosphorylation (top) or PAK1 (K420) acetylation (bottom). And OS was determined using Kaplan-Meier plots
